SpringMVC学习实战_yukiyama
学习自: 【尚硅谷】SpringMVC教程丨一套快速上手spring mvc 。
本文是基于上述视频教程的文字总结,大幅修改了原视频配套文档,并在其基础上及新增部分内容。本文所有代码及其他实验演示素材均存放于 springmvc_in_action 仓库中。
建议先克隆该仓库到本地,一边阅读本文,一边对照每一份代码进行学习。
SpringMVC 是 Spring 家族中用于构建 Web 应用程序的框架,其实现遵循 Model-View-Controller 架构。SpringMVC 以 Spring 框架为基础,因此可利用 Spring 框架中实现的 IoC 容器。
概述
MVC
MVC 是一种软件应用架构思想,将软件应用按照 模型、视图、控制器 来划分。
M:Model,模型层,指工程中的 JavaBean,作用是处理数据。JavaBean 分为两类。
V:View,视图层,指工程中的 html 或 jsp 等页面,作用是与用户进行交互,展示数据。
C:Controller,控制层,指工程中的 servlet,作用是接收请求和响应浏览器。
MVC 的工作流程:
SpringMVC
SpringMVC 是 Spring 的子项目,是 Spring 为表述层开发提供的一整套完备的解决方案。在表述层框架历经 Strust、WebWork、Strust2 等诸多产品的历代更迭之后,目前业界普遍选择了 SpringMVC 作为 JavaEE 项目 表述层 开发的首选方案。
注:三层架构分为表述层(或表示层)、业务逻辑层、数据访问层,表述层表示前台页面和后台 servlet 。
SpringMVC 具有以下特点。
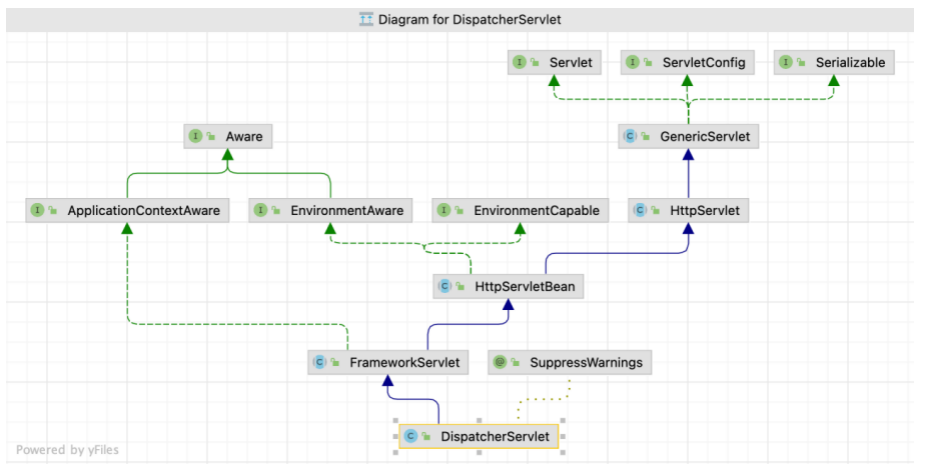
Spring 家族原生产品 ,与 IOC 容器等基础设施无缝对接。基于原生的 Servlet ,通过了功能强大的 前端控制器 DispatcherServlet ,对请求和响应进行统一处理。表述层各细分领域需要解决的问题 全方位覆盖 ,提供 全面解决方案 。
代码清新简洁 ,大幅度提升开发效率。内部组件化程度高,可插拔式组件 即插即用 ,想要什么功能配置相应组件即可。
性能卓著 ,尤其适合现代大型、超大型互联网项目要求。
入门示例
本节展示如何利用 SpringMVC 创建并运行一个 Web 项目。构建和运行环境如下。
1 2 3 4 5 IDE:IntelliJ IDEA 2022.2.1 (Ultimate Edition) 项目构建工具:apache-maven-3.8.5 服务器:apache-tomcat-8.5.82 SpringMVC 版本:5.3.1 浏览器:Chrome
创建maven工程
在 idea 中创建 maven 工程 springmvc_in_action ,archetype 选择maven-archetype-quickstart (将其建为 maven 工程是为了方便统一管理后续子工程的依赖)。接着在该工程下创建模块 springmvc-demo1 ,archetype 选择 maven-archetype-webapp 。创建后手动删除 index.jsp 和 web.xml 文件 (稍后手动添加 web.xml) 。通过 File > Project Structure > Modules 菜单添加 Development Descriptors ,即 web.xml 。
※ Maven 的使用以及父子工程间依赖继承相关的知识可参考 该仓库 的 Maven学习实战_yukiyama 教程。
在 springmvc_in_action 的 pom.xml 中添加如下如下依赖。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 <dependencyManagement > <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > junit</groupId > <artifactId > junit</artifactId > <version > 4.13.2</version > <scope > test</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-webmvc</artifactId > <version > 5.3.1</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > ch.qos.logback</groupId > <artifactId > logback-classic</artifactId > <version > 1.2.3</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > javax.servlet</groupId > <artifactId > javax.servlet-api</artifactId > <version > 3.1.0</version > <scope > provided</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.thymeleaf</groupId > <artifactId > thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId > <version > 3.0.12.RELEASE</version > </dependency > </dependencies > </dependencyManagement >
对应地,在 springmvc-demo1 的 pom.xml 中继承上述依赖。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > junit</groupId > <artifactId > junit</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-webmvc</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > ch.qos.logback</groupId > <artifactId > logback-classic</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > javax.servlet</groupId > <artifactId > javax.servlet-api</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.thymeleaf</groupId > <artifactId > thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId > </dependency > </dependencies >
借助 Maven 中依赖的的传递性,由上述依赖即可导入所有所需依赖。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 [INFO] --- maven-dependency-plugin:2.8:tree (default-cli) @ springmvc-demo1 --- [INFO] com.yukiyama.mvc:springmvc-demo1:war:1.0-SNAPSHOT [INFO] +- junit:junit:jar:4.13.2:test [INFO] | \- org.hamcrest:hamcrest-core:jar:1.3:test [INFO] +- org.springframework:spring-webmvc:jar:5.3.1:compile [INFO] | +- org.springframework:spring-aop:jar:5.3.1:compile [INFO] | +- org.springframework:spring-beans:jar:5.3.1:compile [INFO] | +- org.springframework:spring-context:jar:5.3.1:compile [INFO] | +- org.springframework:spring-core:jar:5.3.1:compile [INFO] | | \- org.springframework:spring-jcl:jar:5.3.1:compile [INFO] | +- org.springframework:spring-expression:jar:5.3.1:compile [INFO] | \- org.springframework:spring-web:jar:5.3.1:compile [INFO] +- ch.qos.logback:logback-classic:jar:1.2.3:compile [INFO] | +- ch.qos.logback:logback-core:jar:1.2.3:compile [INFO] | \- org.slf4j:slf4j-api:jar:1.7.25:compile [INFO] +- javax.servlet:javax.servlet-api:jar:3.1.0:provided [INFO] \- org.thymeleaf:thymeleaf-spring5:jar:3.0.12.RELEASE:compile [INFO] \- org.thymeleaf:thymeleaf:jar:3.0.12.RELEASE:compile [INFO] +- org.attoparser:attoparser:jar:2.0.5.RELEASE:compile [INFO] \- org.unbescape:unbescape:jar:1.1.6.RELEASE:compile
通过 idea 的 maven 工具界面还能看到依赖被排除的重复依赖。
web.xml配置
注册 SpringMVC 的前端控制器 DispatcherServlet 。根据是否要自定义 SpringMVC 配置文件的名称及位置,可分为默认配置方式和扩展配置方式。
默认配置方式
此配置下 (不使用 <init-param> 标签) ,SpringMVC 的配置文件默认位于 WEB-INF 下,默认名称为 <servlet-name>-servlet.xml ,例如,以下配置所对应 SpringMVC 的配置文件位于 WEB-INF下,文件名为 springMVC-servlet.xml 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 <servlet > <servlet-name > springMVC</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > springMVC</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping >
扩展配置方式
可通过 init-param 标签设置 SpringMVC 配置文件的位置和名称,通过 load-on-startup 标签设置 SpringMVC 前端控制器 DispatcherServlet 的初始化时机。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 <servlet > <servlet-name > springMVC</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class > <init-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > classpath:springMVC.xml</param-value > </init-param > <load-on-startup > 1</load-on-startup > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > springMVC</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping >
※ <url-pattern> 标签中使用 / 和 /* 的区别:/ 所匹配的请求可以是 /login 或 .html 或 .js 或 .css 方式的请求路径,但是不能匹配 .jsp 请求路径的请求。因此可以避免在访问 .jsp 页面时,被 DispatcherServlet 处理,导致找不到相应的页面。/* 能够匹配所有请求,例如在使用过滤器时,若需要对所有请求进行过滤,就需要使用 /* 的写法。
springMVC.xml配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 <context:component-scan base-package ="com.atguigu.mvc.controller" /> <bean id ="viewResolver" class ="org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver" > <property name ="order" value ="1" /> <property name ="characterEncoding" value ="UTF-8" /> <property name ="templateEngine" > <bean class ="org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine" > <property name ="templateResolver" > <bean class ="org.thymeleaf.spring5.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver" > <property name ="prefix" value ="/WEB-INF/templates/" /> <property name ="suffix" value =".html" /> <property name ="templateMode" value ="HTML5" /> <property name ="characterEncoding" value ="UTF-8" /> </bean > </property > </bean > </property > </bean > <mvc:default-servlet-handler /> <mvc:annotation-driven > <mvc:message-converters > <bean class ="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter" > <property name ="defaultCharset" value ="UTF-8" /> <property name ="supportedMediaTypes" > <list > <value > text/html</value > <value > application/json</value > </list > </property > </bean > </mvc:message-converters > </mvc:annotation-driven >
编写HTML页面
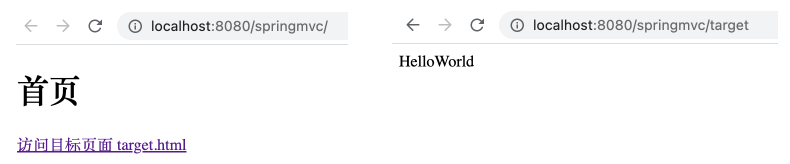
首先编写项目主页 index.html ,在该页中有一链接可跳转到 target.html 页面。
index.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thyemleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 首页</title > </head > <body > <h1 > 首页</h1 > <a th:href ="@{/target}" > 访问目标页面 target.html</a > </body > </html >
target.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > </head > <body > HelloWorld </body > </html >
创建请求控制器
前端控制器对浏览器发送的请求进行了统一的处理,将具体的请求交给不同的 请求控制器 处理。请求控制器中每一个处理请求的方法称为 控制器方法 。
因为 SpringMVC 的控制器由 POJO 担任,因此需要通过 @Controller 注解将其标识为一个 控制层组件 ,交给 Spring 的 IoC 容器管理,此时 SpringMVC 才能够识别控制器的存在。
1 2 @Controller public class HelloController {}
访问页面
在请求控制器中类 HelloController 中创建处理请求的方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @RequestMapping("/") public String index () { return "index" ; }
页面跳转
在请求控制器类中创建处理请求的方法
1 2 3 4 @RequestMapping("/hello") public String HelloWorld () { return "target" ; }
测试
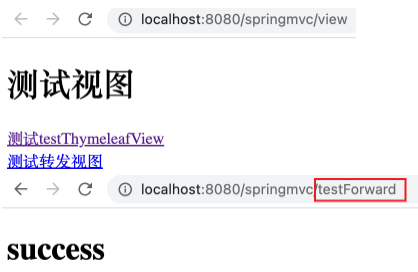
在 Tomcat 中部署 springmvc-demo1 应用。浏览器打开 http://localhost:8080/springmvc/ ,点击其中的超链接后可以跳转到相应页面。
※ Tomcat 部署应用的设置方法请参考 该仓库 的 JavaWeb学习实战_yukiyama.md 教程的「Tomcat」一节。
总结 SpringMVC 处理请求的主要过程如下。
Web 服务器 (Tomcat) 启动时创建 DispatcherServlet 实例 (通常在 web.xml 中通过 <load-on-startup> 标签将其设置为随 Web 服务器启动而创建) 。
浏览器发送请求,若请求地址符合前端控制器的 url-pattern ,该请求就会被前端控制器 DispatcherServlet 处理。
前端控制器会读取 SpringMVC 的核心配置文件,通过扫描组件找到控制器。
控制器匹配请求地址与 @RequestMapping 注解的 value 属性值,若匹配成功,该注解所标识的控制器方法就是处理请求的方法。处理请求的方法返回字符串类型的视图名称。
控制器方法返回的视图名称由视图解析器解析,加上前缀和后缀组成视图的路径,通过 Thymeleaf 对视图进行渲染,最终转发到视图所对应页面。
@RequestMapping
@RequestMapping ,「请求映射」注解,用于关联请求与处理请求的控制器方法。SpringMVC 接收到指定的请求后,根据关联关系找到对应的控制器方法来处理该请求。@RequestMapping 可作为类注解或方法注解,作用分别为。
作为类注解时:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始路径段。
作为方法注解时:设置映射请求请求路径的具体路径段。
本节我们创建 springMVC-demo2 子项目演示如何使用 @RequestMapping 注解。
首先在该项目下新建 TestController.java 控制器。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package com.yukiyama.mvc.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@Controller public class TestController { @RequestMapping("/") public String index () { return "index" ; } }
接着编写 web.xml 、springMVC.xml ,内容与「入门示例」相同。
最后编写如下 index.html 页面。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thyemleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 首页</title > </head > <body > <h1 > 首页</h1 > </body > </html >
与「入门示例」一样,运行该项目后通过 http://localhost:8080/springmvc/ 能够正常打开 index.html 页面。
属性
@RequestMapping 作为方法注解时,主要有如下属性。
@RequestMapping 方法注解属性
描述
value
默认属性,必须设置。类型为 String[] 数组,表示匹配该数组指定请求地址的请求。
method
类型为 RequestMethod[] 数组,表示匹配该数组指定的请求类型的请求。不设置该属性时可匹配所有类型请求。
params
类型为 String[] 数组,表示匹配的请求中的参数要符合该属性指定的参数规则。
headers
类型为 String[] 数组,表示匹配的请求的 Headers 要符合该属性指定的 Headers 规则。
在 springMVC-demo2 中创建 RequestMappingController.java 控制器,在其中编写不同的控制器方法观察不同属性的作用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 package com.yukiyama.mvc.controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@Controller public class RequestMappingController {}
value
@RequestMapping 注解的默认属性为 value 。value 为字符串类型数组,表示其注解的方法能够匹配 value 数组指定的多个请求地址。在 RequestMappingController 类添加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 @RequestMapping("/") public String index () { return "index" ; }
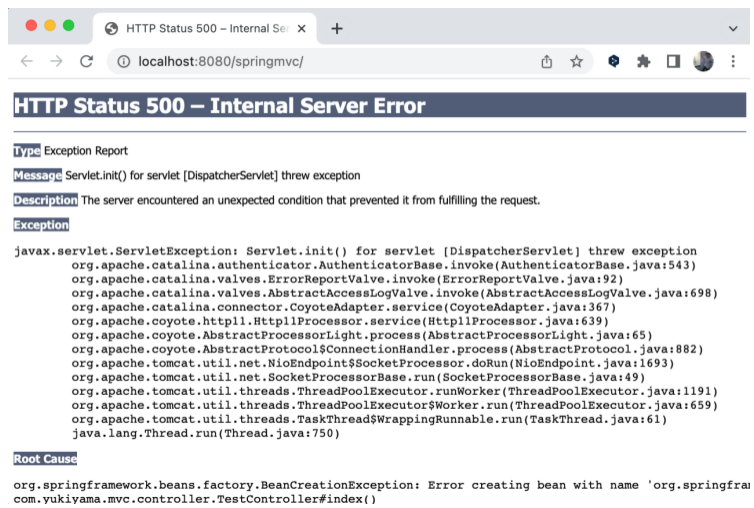
运行项目后发现页面出现 500 错误。
控制台打印的错误信息中可看到如下描述,原因是当前有两个控制器 TestController 和 RequestMappingController ,均有一个匹配 / 路径的 index 方法。这说明所有控制器的控制器方法所映射的请求地址必须是唯一的,也就是对于一个请求地址,要保证只有一个控制器方法来处理。
1 2 3 4 ... to { [/]}: There is already 'requestMappingController' bean method com.yukiyama.mvc.controller.RequestMappingController#index() mapped. ...
将 value 中的请求地址修改为其他即可。如下给出本例的控制器和 index.html, success.html 。
RequestMappingController.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 package com.yukiyama.mvc.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@Controller @RequestMapping("/hello") public class RequestMappingController { @RequestMapping("/testRequestMapping") public String success () { return "success" ; } }
index.html
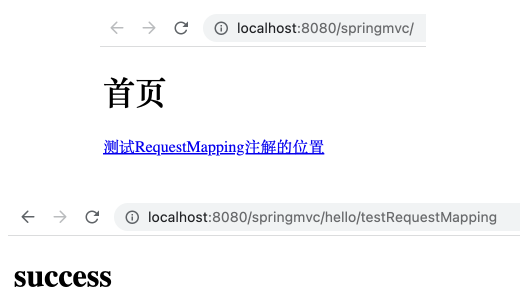
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thyemleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 首页</title > </head > <body > <h1 > 首页</h1 > <a th:href ="@{/hello/testRequestMapping}" > 测试RequestMapping注解的位置</a > <br > </body > </html >
success.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thyemleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > </title > </head > <body > <h1 > success</h1 > </body > </html >
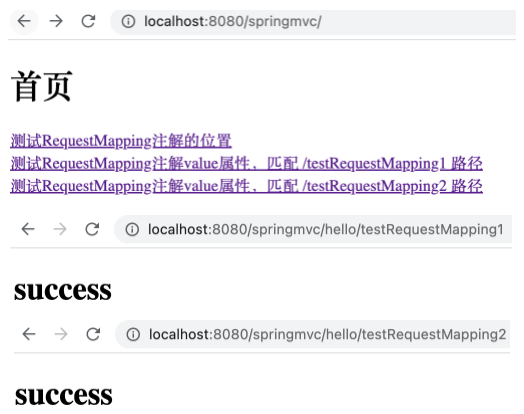
项目运行后打开 index.html ,点击链接能够跳转到 success.html 页面。该页面路径中的 /hello 即控制器类注解 @RequestMapping 中设置的属性值,而 /testRequestMapping 是方法注解 @RequestMapping 中设置的属性值。
由此可以看到,类注解 @RequestMapping 属性中设置的路径段可视作该控制器对应的请求路径的统一前缀。例如响应注册操作的注册控制器的类注解 @RequestMapping 的属性可为 /register ,则所有与注册相关的请求路径信息都是形如 http://localhost:8080/register/... 这样的形式。
假设还有用户控制器,且注册控制器和用户控制器中都存在 add 方法分别用于处理 http://.../register/add 和 http://.../user/add 请求,则类注解的路径段就可以提前区别是哪个功能模块的请求,不同控制器内就可以有相同子路径段的控制器方法了。
value 为字符串数组类型,可支持多个不同的路径段,使同一个控制器方法对应多个不同的请求路径。如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @RequestMapping( value = {"/testRequestMapping", "/testRequestMapping1", "/testRequestMapping2"} ) public String success () { return "success" ; }
在 index.html 的 <body> 标签中新增两条对应 /testRequestMapping1和 /testRequestMapping2 的链接。
1 2 3 <a th:href ="@{/hello/testRequestMapping}" > 测试RequestMapping注解的位置</a > <br > <a th:href ="@{/hello/testRequestMapping1}" > 测试RequestMapping注解value属性,匹配 /testRequestMapping1 路径</a > <br > <a th:href ="@{/hello/testRequestMapping2}" > 测试RequestMapping注解value属性,匹配 /testRequestMapping2 路径</a > <br >
运行项目,可以看到控制器方法中 value 属性的多个路径段值,确实使该方法映射到了相应的不同请求路径。
ant风格路径
value 属性值可写为 ant 风格的模糊匹配形式,主要匹配规则如下。
通配符
描述
?表示任意的单个字符,但不支持 / 和 ? 。
*表示任意的 0 个或多个字符,但不支持 / 和 ? 。
**以 /**/xxx/ 的形式,表示 0 层或多层目录。
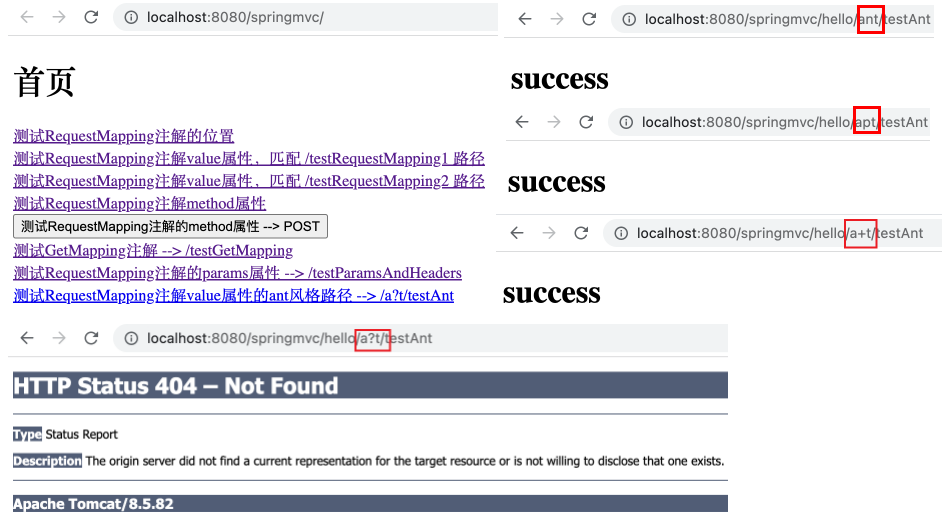
通配符?
表示任意的单个字符,但不支持 / 和 ? 。
在 RequestMappingController 中增加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 @RequestMapping("/a?t/testAnt") public String testAnt () { return "success" ; }
在 index.html 的 <body> 标签中新增如下链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/hello/ant/testAnt}" > 测试RequestMapping注解value属性的ant风格路径 --> /a?t/testAnt</a > <br >
运行项目,可以看到 /a?t 中的 ? 可替换为除少数在路径中的特殊字符外的任意单个字符,都能匹配。
通配符*
表示任意的 0 个或多个字符,但不支持 / 和 ? 。与 ? 用法类似,示例略。
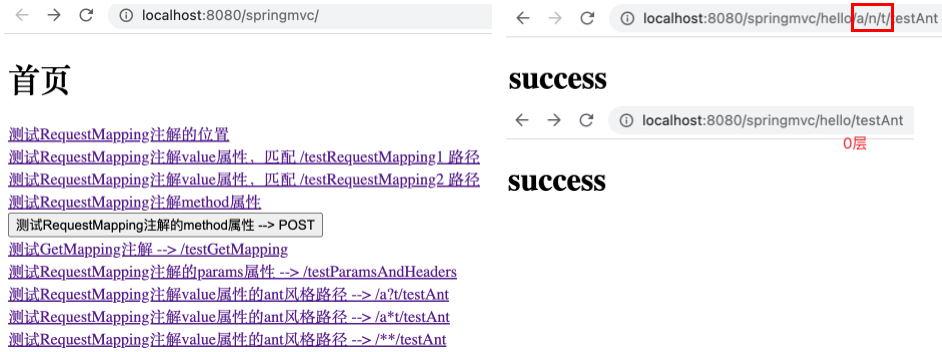
通配符**
以 /**/xxx/ 的形式,表示任意的一层或多层目录。
修改 value 属性为 @RequestMapping("/**/testAnt") ,在 index.html 的 <body> 标签中新增如下链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/hello/ant/testAnt}" > 测试RequestMapping注解value属性的ant风格路径 --> /**/testAnt</a > <br >
运行项目后,效果如下。
路径中的占位符
路径传参的原始方式 /deleteUser?id=1 ,Restful 风格为 /deleteUser/1 。SpringMVC 路径中的占位符常用于 RESTful 风格中,将请求路径中将某些数据通过路径的方式传输到服务器中,可以在相应的 @RequestMapping 注解的 value 属性中通过占位符 {} 表示传输的数据,再配合参数注解 @PathVariable 将占位符所表示的数据赋值给控制器方法的形参。
在 RequestMappingController 中增加如下方法。
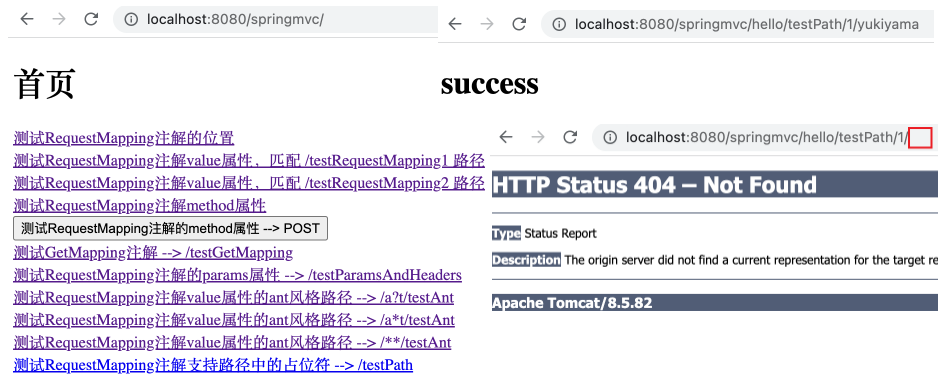
1 2 3 4 5 6 @RequestMapping("/testPath/{id}/{username}") public String testPath (@PathVariable("id") Integer id, @PathVariable("username") String username) { System.out.println("id = " + id + ", username = " + username); return "success" ; }
在 index.html 的 <body> 标签中新增如下链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/hello/testPath/1/yukiyama}" > 测试RequestMapping注解支持路径中的占位符 --> /testPath</a > <br >
运行项目后,打开链接后控制台输出 id = 1, username = yukiyama 。尝试在 URL 中删除 yukiyama 再请求,将返回 404 错误,这说明占位符不可为空。
method
@RequestMapping 方法注解的 method 属性用于匹配请求类型。设置该属性时,首先请求路径要与其所注解的控制器方法的 value 属性向匹配,接着要匹配该属性设置的请求类型值,设置多个时只需匹配其中之一即可,若全部不匹配,则返回 错误。不设置该属性时,匹配所有请求类型。
method 属性为如下枚举类型 RequestMethod ,可以看到其中支持的请求类型。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 package org.springframework.web.bind.annotation;public enum RequestMethod { GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTIONS, TRACE; private RequestMethod () { } }
在 RequestMappingController 的 success 方法注解 @RequestMapping 中加入 method 属性,如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @RequestMapping( value = {"/testRequestMapping", "/testRequestMapping1", "/testRequestMapping2", "/testMethod"}, method = {RequestMethod.GET} ) public String success () { return "success" ; }
在 index.html 的 <body> 标签中增加 POST 类型的表单。
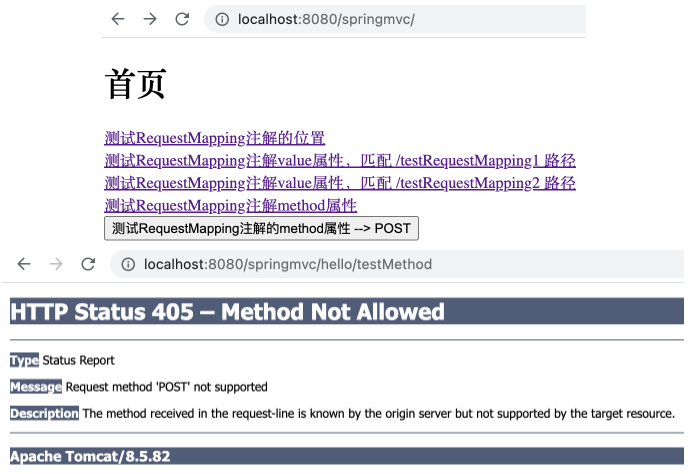
1 2 3 4 <a th:href ="@{/hello/testMethod}" > 测试RequestMapping注解method属性</a > <br > <form th:action ="@{/hello/testMethod}" method ="post" > <input type ="submit" value ="测试RequestMapping注解的method属性 --> POST" > </form >
※ 需要注意 form 表单中的 method 只支持 post 与 get,若写为其他类型,如 put ,则按照默认的 get 处理。
由于表单中的请求类型为 POST ,与 method 属性中指定的请求类型 GET 不一致,运行项目,在 index.html 页面上点击 submit 按钮会出现 405 错误。
需要在 method 属性中增加对 POST 类型请求的匹配即可。
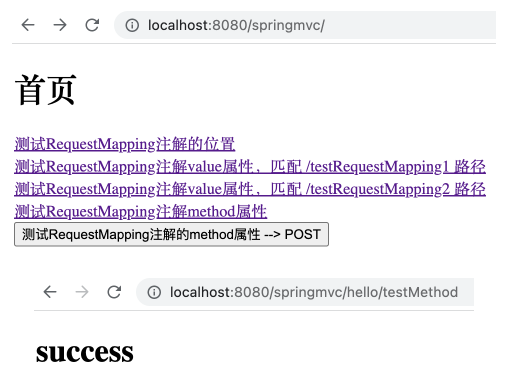
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @RequestMapping( value = {"/testRequestMapping", "/testRequestMapping1", "/testRequestMapping2", "/testMethod"}, method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST} ) public String success () { return "success" ; }
调整后可正常跳转。
@XxxMapping
当明确了要匹配的请求类型时,可以使用如下指定了请求类型的 请求映射方法注解 来替代 @RequestMapping 方法注解。由该注解标注的方法所匹配的请求,必须是该注解指定的请求类型。
1 2 3 4 @GetMapping @PostMapping @DeleteMapping @PutMapping
在 RequestMappingController 中添加如下方法测试 @GetMapping 的效果。
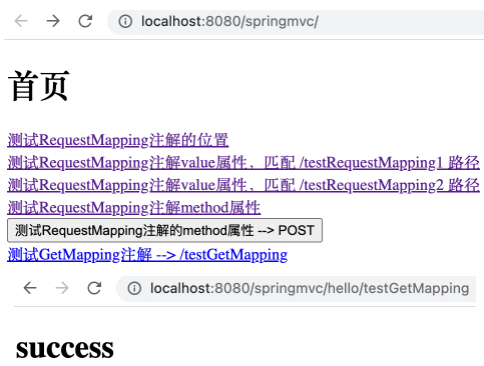
1 2 3 4 @GetMapping("/testGetMapping") public String testGetMapping () { return "success" ; }
在 index.html 的 <body> 标签内增加如下内容。
1 <a th:href ="@{/hello/testGetMapping}" > 测试GetMapping注解 --> /testGetMapping</a > <br >
运行并点击相应的超链接,由于超链接为 Get 请求,与 @GetMapping 相匹配,可正常跳转。
params
params 属性类型为 String[] 数组,表示匹配的请求中的参数要符合该属性指定的参数规则。
参数匹配规则
描述
param要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带 param 请求参数。
!param要求请求映射所匹配的请求不能携带 param 请求参数。
param=value要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带 param 请求参数且 param=value 。
param!=value要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带 param 请求参数且 param!=value 。
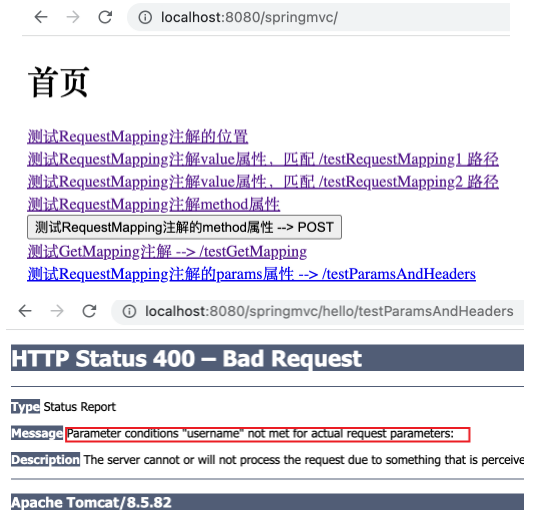
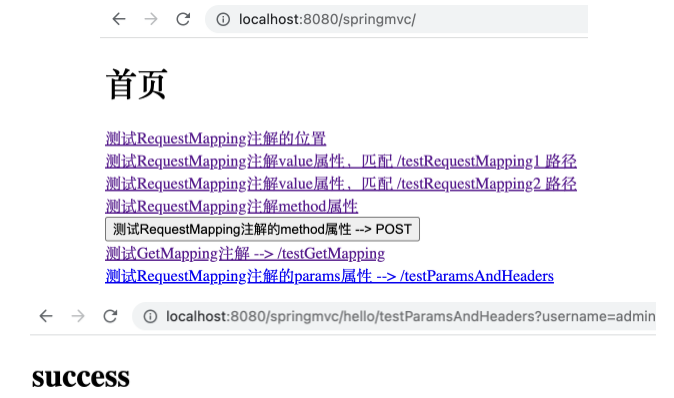
在 RequestMappingController 中新建 testParamsAndHeaders 方法如下,其中 @RequestMapping 注解中加入属性 params 并设置一个 usename 表示匹配的请求需携带该参数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @RequestMapping( value = {"/testParamsAndHeaders"}, params = {"username"} ) public String testParamsAndHeaders () { return "success" ; }
在 index.html 的 <body> 中新增如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/hello/testParamsAndHeaders}" > 测试RequestMapping注解的params属性 --> /testParamsAndHeaders</a > <br >
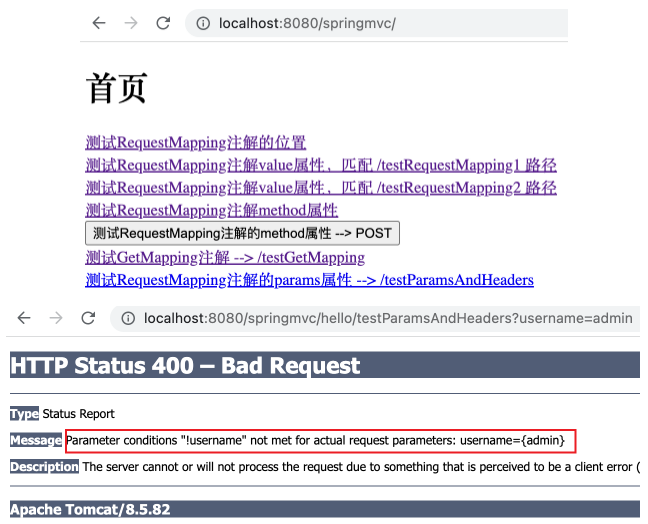
运行应用,点击上述超链接后出现 400 错误。从错误 message 中可以看到未匹配到指定参数导致请求失败。
修改 index.html 中前述超链接如下,加入所需参数。
1 <a th:href ="@{/hello/testParamsAndHeaders(username='admin'}" > 测试RequestMapping注解的params属性 --> /testParamsAndHeaders</a > <br >
修改后重新运行应用,可正常跳转。
若将 @RequestMapping 中的 params 改为 params = {"!username"} ,则出现如下 400 错误。
params 可以配置多个参数。例如将 index.html 的前述超链接改为如下。
1 <a th:href ="@{/hello/testParamsAndHeaders(username='admin',password=12345)}" > 测试RequestMapping注解的params属性 --> /testParamsAndHeaders</a >
params 改为 params = {"username", "password=12345"} ,可成功匹配。
与 params 属性用法类似,但匹配的是请求头部信息。
参数匹配规则
描述
param要求请求映射所匹配的请求的 Headers 中必须携带 param 参数。
!param要求请求映射所匹配的请求的 Headers 中不能携带 param 参数。
param=value要求请求映射所匹配的请求的 Headers 中必须携带 param 参数且 param=value 。
param!=value要求请求映射所匹配的请求的 Headers 中必须携带 param 参数且 param!=value 。
在 RequestMappingController 的 testParamsAndHeaders 方法的 @RequestMapping 注解中加入属性 headers 并设置一个 Host 表示匹配的请求的头部信息中需携带该参数且其值必须为 localhost:8081 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @RequestMapping( value = {"/testParamsAndHeaders"}, params = {"username", "password=12345"}, headers = {"Host=localhost:8081"} ) public String testParamsAndHeaders () { return "success" ; }
由于 Tomcat 默认端口为 8080,因此运行项目,点击相应超链接后出现如下 404 错误。
改为 headers = {"Host=localhost:8080"} 后即可正常访问。
获取请求参数
当请求匹配到控制器方法后,有多种方法可获取到该请求的请求参数。
首先在 TestController 中加入如下方法。
1 2 3 4 @RequestMapping("/param") public String param () { return "test_param" ; }
新建 test_param.html 页面。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thymeleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 测试请求参数</title > </head > <body > <h1 > 测试请求参数</h1 > </body > </html >
新建 ParamController.java 控制器。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 package com.yukiyama.mvc.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;@Controller public class ParamController {}
后续在 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/param 页面中通过点击不同链接完成本节测试。
通过ServletAPI
将 HttpServletRequest request 作为控制器方法的形参,此时 request 为封装了当前请求的请求报文的对象。
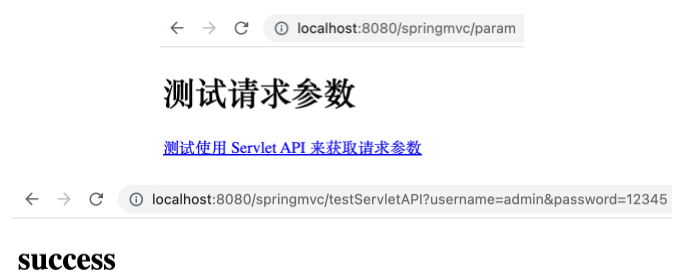
在 ParamController 中新建 testServletAPI 方法如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @RequestMapping("/testServletAPI") public String testServletAPI (HttpServletRequest request) { String username = request.getParameter("username" ); String password = request.getParameter("password" ); System.out.println("username = " + username + ", password = " + password); return "success" ; }
在 test_param.html 的 <body> 中新增如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testServletAPI(username='admin',password=12345)}" > 测试使用 Servlet API 来获取请求参数</a > <br >
运行项目,访问 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/param ,可以访问上述链接,且控制台打印 username = admin, password = 12345 ,表明获取到了指定的参数。
通过控制器方法形参
在控制器方法的形参位置,设置 与请求参数同名的形参 ,当浏览器发送请求,匹配到请求映射时,DispatcherServlet 就会将请求参数赋值给相应的形参。
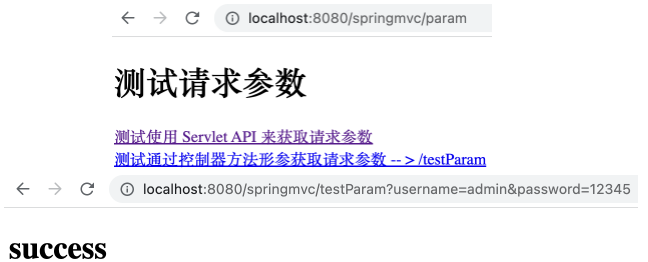
在 ParamController 中新建 testParam 方法如下。
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/testParam") public String testParam (String username, String password) { System.out.println("username = " + username + ", password = " + password); return "success" ; }
在 test_param.html 的 <body> 中新增如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testParam(username='admin',password=12345)}" > 测试通过控制器方法形参获取请求参数 -- > /testParam</a > <br >
运行项目,访问 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/param ,可以访问上述链接,且控制台打印 username = admin, password = 12345 ,表明获取到了指定的参数。
多个同名参数
当请求参数中有多个同名参数时 (例如 checkbox 元素) ,若控制器方法对应形参为 String 类型,则得到这些同名参数以 , 分隔的拼接字符串;若为 String[] 类型,则这些同名参数值为数组中的元素。
在 ParamController 中修改 testParam 方法如下。
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/testParam") public String testParam (String username, String password, String hobby) { System.out.println("username = " + username + ", password = " + password + ", hobby = " + hobby); return "success" ; }
在 test_param.html 的 <body> 中新增如下表单。
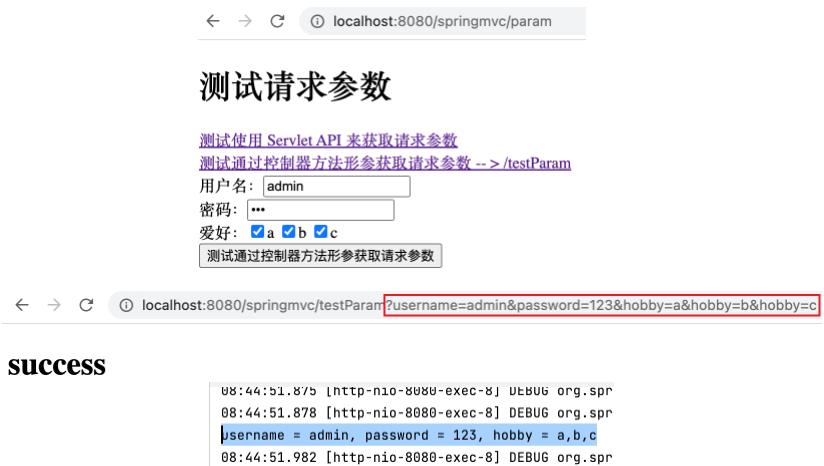
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <form th:action ="@{/testParam}" method ="get" > 用户名:<input type ="text" name ="username" > <br > 密码:<input type ="password" name ="password" > <br > 爱好:<input type ="checkbox" name ="hobby" value ="a" > a <input type ="checkbox" name ="hobby" value ="b" > b <input type ="checkbox" name ="hobby" value ="c" > c<br > <input type ="submit" value ="测试通过控制器方法形参获取请求参数" > </form >
运行项目,访问 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/param ,填写表单并点击 测试通过控制器方法形参获取请求参数 提交,可成功跳转,且控制台打印 username = admin, password = 123, hobby = a,b,c ,表明获取到了指定的参数且 hobby 的值为三个同参数名参数值的拼接结果。
将 testParam 方法中的 hobby 改为 String[] 类型,如下。
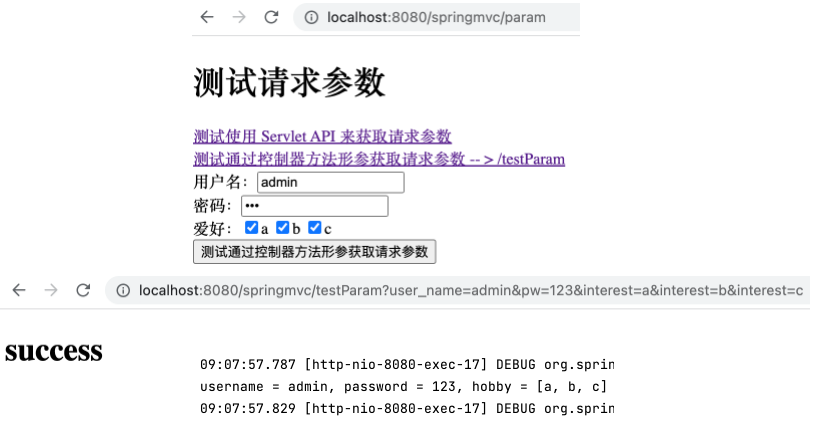
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/testParam") public String testParam (String username, String password, String[] hobby) { System.out.println("username = " + username + ", password = " + password + ", hobby = " + Arrays.toString(hobby)); return "success" ; }
再次运行项目,填入表单点击提交按钮,跳转成功,且控制台打印 username = admin, password = 123, hobby = [a, b, c] 。可以看到 hobby 为字符串数组。
@RequestParam
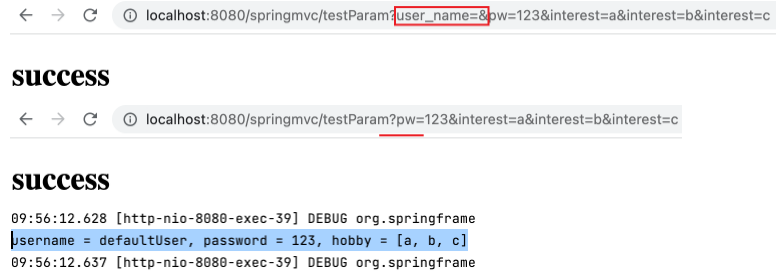
通过控制器方法形参获取请求参数,默认情况下要求控制器方法形参要与请求参数的参数名一致,不一致则无法获取 (为 null) 。例如在前述项目保持运行的情况下,访问如下 URL (username 改为了 user_name) ,则控制台输出 username = null, password = 123, hobby = a,b,c 。
1 http://localhost:8080/springmvc/testParam?user_name=admin&password=123&hobby=a&hobby=b&hobby=c
可使用 SpringMVC 提供的 @RequestParam 参数注解将请求参数名映射到控制器方法形参名。
value属性
在 ParamController 中修改 testParam 方法如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @RequestMapping("/testParam") public String testParam ( @RequestParam("user_name") String username, @RequestParam("pw") String password, @RequestParam("interest") String[] hobby) { System.out.println("username = " + username + ", password = " + password + ", hobby = " + Arrays.toString(hobby)); return "success" ; }
在 test_param.html 的 <body> 中修改表单如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <form th:action ="@{/testParam}" method ="get" > 用户名:<input type ="text" name ="user_name" > <br > 密码:<input type ="password" name ="pw" > <br > 爱好:<input type ="checkbox" name ="interest" value ="a" > a <input type ="checkbox" name ="interest" value ="b" > b <input type ="checkbox" name ="interest" value ="c" > c<br > <input type ="submit" value ="测试通过控制器方法形参获取请求参数" > </form >
运行项目,访问 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/param ,填写表单并点击 测试通过控制器方法形参获取请求参数 提交,可成功跳转,且控制台打印 username = admin, password = 123, hobby = [a, b, c] ,表明请求参数通过 @RequestParam 映射到控制器形参,从而获取到参数。
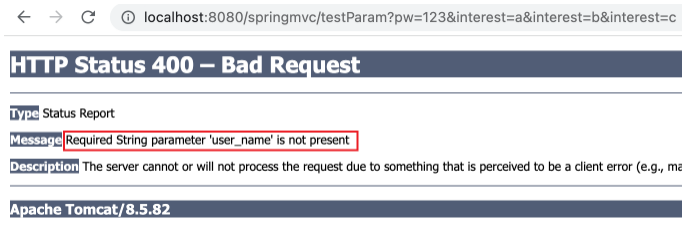
required属性
@RequestParam 的 required 属性表示是否必须存在所要映射的请求参数,默认值为 true,则当请求参数缺少 value 所指定的的参数时将出现 400 错误。如下,请求参数中缺少 user_name=admin ,返回 400 错误页面中可看到 Required String parameter 'user_name' is not present 。
可通过设置 required 属性为 false,使得缺少对应请求参数时也能够执行相应的控制器方法。将 testParam 方法改为如下。
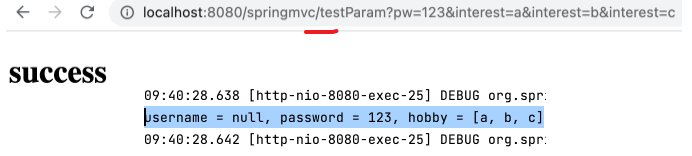
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @RequestMapping("/testParam") public String testParam ( @RequestParam(value = "user_name", required = false) String username, @RequestParam("pw") String password, @RequestParam("interest") String[] hobby) { System.out.println("username = " + username + ", password = " + password + ", hobby = " + Arrays.toString(hobby)); return "success" ; }
去掉 url 中的 user_name=admin& ,可成功打开页面,此时控制台输出 username = null, password = 123, hobby = [a, b, c] ,可见在 required = false 时,若无对应请求参数,则控制器中对应的形参被赋值为 null 。
defaultValue属性
无论 required 属性值为 true 或 false ,当请求未携带 value 所指定的请求参数或该请求参数值为 "" (空字符串) 时,使用 defaultValue 属性值为形参赋值。
将 testParam 方法改为如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @RequestMapping("/testParam") public String testParam ( @RequestParam( value = "user_name", required = false, defaultValue = "defaultUser" ) String username, @RequestParam("pw") String password, @RequestParam("interest") String[] hobby) { System.out.println("username = " + username + ", password = " + password + ", hobby = " + Arrays.toString(hobby)); return "success" ; }
去掉 url 中的 user_name=admin& 或改为 user_name=& (参数为空字符串),可成功打开页面,此时控制台输出 username = defaultUser, password = 123, hobby = [a, b, c] 。
@RequestHeader 参数注解创建请求头信息和控制器方法形参的映射关系。@RequestHeader 注解的三个属性 value, required, defaultValue 用法同 @RequestParam 。
将 testParam 方法改为如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @RequestMapping("/testParam") public String testParam ( @RequestParam( value = "user_name", required = false, defaultValue = "defaultUser" ) String username, @RequestParam("pw") String password, @RequestParam("interest") String[] hobby, @RequestHeader( value = "Host", required = false, defaultValue = "localhost:8080" ) String host) System.out.println("username = " + username + ", password = " + password + ", hobby = " + Arrays.toString(hobby)); System.out.println("host = " + host); return "success" ; }
由于请求中的 Headers 中有 Host ,且其值为 localhost:8080 。因此运行项目,访问 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/param ,填写表单并点击 测试通过控制器方法形参获取请求参数 提交,可成功跳转,且控制台打印如下。
1 2 username = admin, password = 123, hobby = [a, b, c] host = localhost:8080
@CookieValue
@CookieValue 参数注解创建请求头信息和控制器方法形参的映射关系。@CookieValue 注解的三个属性 value, required, defaultValue 用法同 @RequestParam 。
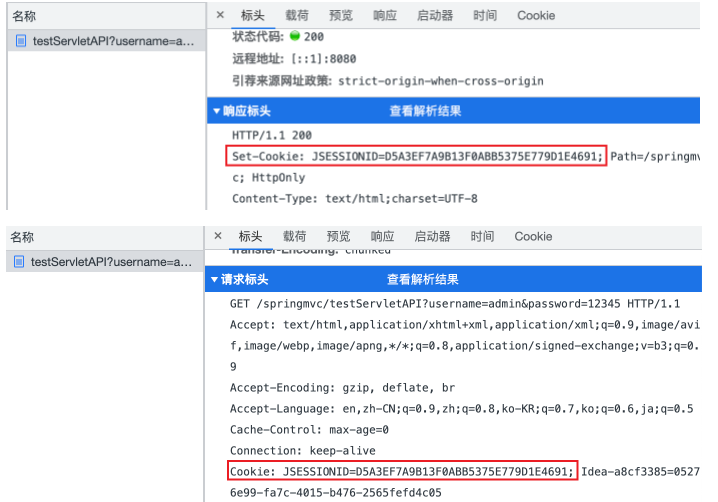
要测试 @CookieValue ,首先需要生成 cookie。可以在 testServletAPI 方法中加入 request.getSession() 方法来获取 session。如下是修改后的 testServletAPI 方法。如在「通过ServletAPI获取」一节中那样,访问 http://localhost:8080/springmvc/testServletAPI?username=admin&password=12345 之后,该请求的返回报文 Headers 中就会记录 session 信息,并将其作为下次请求时携带的 cookie 。
※ session 与 cookie 的关系请参考 该仓库 的 JavaWeb学习实战_yukiyama.md 教程的「session」一节中的「session与cookie」。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @RequestMapping("/testServletAPI") public String testServletAPI (HttpServletRequest request) { HttpSession session = request.getSession(); String username = request.getParameter("username" ); String password = request.getParameter("password" ); System.out.println("username = " + username + ", password = " + password); return "success" ; }
第一次请求时, cookie 信息在该次请求的响应 Headers 中,此时 cookie 已记录在本地浏览器中,并在下次请求时写入请求 Headers 中。如下是第一次请求时的响应 Headers 以及第二次请求的请求 Headers 。
有了 cookie 之后,将 testParam 方法改为如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @RequestMapping("/testParam") public String testParam ( @RequestParam( value = "user_name", required = false, defaultValue = "defaultUser" ) String username, @RequestParam("pw") String password, @RequestParam("interest") String[] hobby, @RequestHeader( value = "Host", required = false, defaultValue = "localhost:8080" ) String host, @CookieValue("JSESSIONID") String jsessionid ) { System.out.println("username = " + username + ", password = " + password + ", hobby = " + Arrays.toString(hobby)); System.out.println("host = " + host); System.out.println("JSESSIONID = " + jsessionid); return "success" ; }
运行项目,访问 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/param ,填写表单并点击 测试通过控制器方法形参获取请求参数 提交,可成功跳转,且控制台打印如下。
1 2 3 username = admin, password = 123, hobby = [a, b, c] host = localhost:8080 JSESSIONID = D5A3EF7A9B13F0ABB5375E779D1E4691
通过控制器方法Bean形参
若需要获取的请求参数与 ORM 对象的字段一一对应,则控制器方法参数可设置为该 ORM 类型,则通过该形参得到的 ORM 对象实例的字段即为请求参数。
在 test_param.html 的 <body> 中新增如下表单。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <form th:action ="@{/testBean}" method ="post" > 用户名:<input type ="text" name ="username" > <br > 密码:<input type ="password" name ="password" > <br > 性别:<input type ="radio" name ="sex" value ="男" > 男<input type ="radio" name ="sex" value ="女" > 女<br > 年龄:<input type ="text" name ="age" > <br > 邮箱:<input type ="text" name ="email" > <br > <input type ="submit" value ="使用POJO接收请求参数" > </form >
在 ParamController 控制器中新增如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/testBean") public String testBean (User user) { System.out.println("user = " + user); return "success" ; }
运行项目,填入参数后可点击提交按钮可正常跳转。
控制台输出如下信息,可看到通过在控制器方法中传入 Bean 对象,将请求参数赋值到了 Bean 对象的对应字段中。但其中 sex 参数值 男 未正确显示,需要处理此编码问题。
1 user = User{id=null, username='admin', password='123', age=20, sex='ç·', email='admin@gmail.com'}
请求参数乱码
若之前的表单的 method 为 get,则不会出现乱码问题。但 method 为 post 出现了汉字无法被正常显示的现象,可以使用 SpringMVC 提供的编码过滤器 CharacterEncodingFilter 解决请求参数中不能正确读取汉字的问题。
在 web.xml 中加入如下内容,即可完成在 CharacterEncodingFilter 中设置请求及响应的编码为 UTF-8 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <filter > <filter-name > CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name > <filter-class > org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class > <init-param > <param-name > encoding</param-name > <param-value > UTF-8</param-value > </init-param > <init-param > <param-name > forceResponseEncoding</param-name > <param-value > true</param-value > </init-param > </filter > <filter-mapping > <filter-name > CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name > <url-pattern > /*</url-pattern > </filter-mapping >
重新运行项目,在表单中填入一些中文,可正确显示。
域对象共享数据
通过作用域对象可在应用中共享数据。后续按照 request、session、application 三个作用域依次讲解如何利用域对象共享数据。为完成演示,先做如下准备工作。
复制之前的 springmvc-demo2 为 springmvcdemo3 子项目。在父项目的 <modules> 标签中加入该子项目,并调整项目下的文件后如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 springmvcdemo3 ├── pom.xml └── src └── main ├── java │ └── com │ └── yukiyama │ └── mvc │ └── controller │ ├── ScopeController.java │ └── TestController.java ├── resources │ └── springMVC.xml └── webapp └── WEB-INF ├── templates │ ├── index.html │ └── success.html └── web.xml
其中 ScopeController 控制器、index.html 、success.html 均为新建 (html 要引入 thymeleaf 命名空间),用于完成后续演示。
ScopeController.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 package com.yukiyama.mvc.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;@Controller public class ScopeController {}
index.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thyemleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 首页</title > </head > <body > <h1 > 共享域对象</h1 > </body > </html >
success.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thyemleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > </title > </head > <body > <h1 > success</h1 > </body > </html >
后续在 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/ 页面中通过点击不同链接完成本节测试。
request域共享
有多种方式在 request 作用域中共享数据。
request域共享方式
共享方法
HttpServletRequestsetAttribute(String name, Object o)
ModelAndViewaddObject(String attributeName, @Nullable Object attributeValue)
ModeladdAttribute(String var1, @Nullable Object var2)
Mapput(K key, V value)
ModelMapaddAttribute(String attributeName, @Nullable Object attributeValue)
ServletAPI
将 HttpServletRequest request 作为控制器方法的形参,此时 request 为当前请求对象,通过该对象的 setAttribute 方法共享 request 域数据。
在 ScopeController 控制器中增加如下方法。
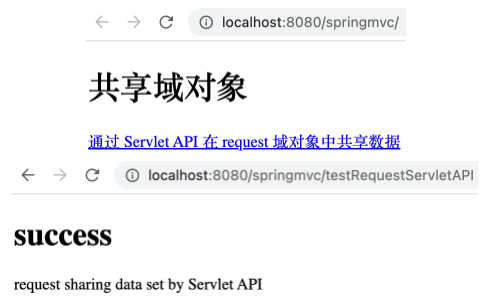
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/testRequestServletAPI") public String testRequestServletAPI (HttpServletRequest request) { request.setAttribute("testRequestScope" , "request sharing data set by Servlet API" ); return "success" ; }
在 index.html 的 <body> 标签中加入如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testRequestServletAPI}" > 通过 Servlet API 在 request 域对象中共享数据</a > <br >
在 success.html 的 <body> 标签中加入如下。
1 <p th:text ="${testRequestScope}" > </p >
运行项目,打开 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/ ,点击相应链接后可看到如下,表明通过 HttpServletRequest 实例对象在 request 作用域下共享了数据。
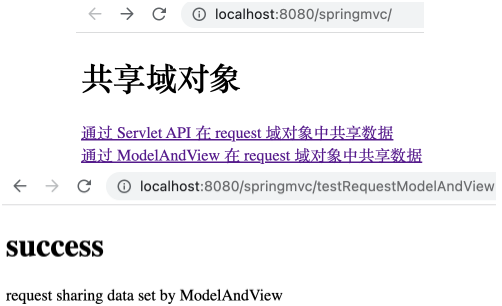
ModelAndView
SpringMVC 提供了 ModelAndView 类来处理模型与视图,可利用其中的实例方法 addObject 向 request 作用域中设置共享数据。
在 ScopeController 控制器中增加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @RequestMapping("/testRequestModelAndView") public ModelAndView testRequestModelAndView () { ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView (); mav.addObject("testRequestScope" , "request sharing data set by ModelAndView" ); mav.setViewName("success" ); return mav; }
在 index.html 的 <body> 标签中加入如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testRequestModelAndView}" > 通过 ModelAndView 在 request 域对象中共享数据</a > <br >
运行项目,打开 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/ ,点击相应链接后可看到如下,表明通过 ModelAndView 实例对象在 request 作用域下共享了数据。
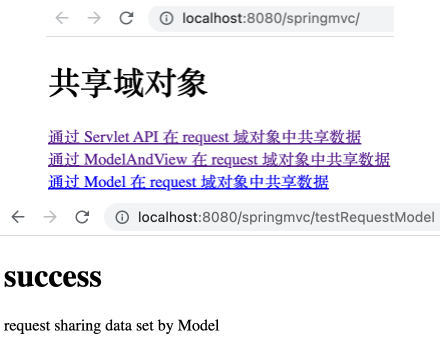
Model
SpringMVC 提供了 Model 类来处理模型,可利用其中的实例方法 addAttribute 向 request 作用域中设置共享数据。
在 ScopeController 控制器中增加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/testRequestModel") public String testRequestModel (Model model) { model.addAttribute("testRequestScope" , "request sharing data set by Model" ); return "success" ; }
在 index.html 的 <body> 标签中加入如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testRequestModel}" > 通过 Model 在 request 域对象中共享数据</a > <br >
运行项目,打开 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/ ,点击相应链接后可看到如下,表明通过 Model 实例对象在 request 作用域下共享了数据。
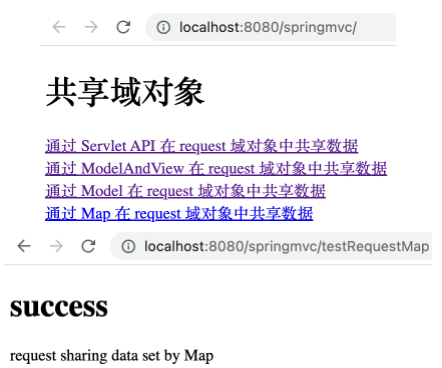
Map
可以在控制器方法中传入 Map 实例,并 put 方法向 request 作用域中设置共享数据。
在 ScopeController 控制器中增加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/testRequestMap") public String testRequestMap (Map<String, Object> map) { map.put("testRequestScope" , "request sharing data set by Map" ); return "success" ; }
在 index.html 的 <body> 标签中加入如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testRequestMap}" > 通过 Map 在 request 域对象中共享数据</a > <br >
运行项目,打开 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/ ,点击相应链接后可看到如下,表明通过 Map 实例对象在 request 作用域下共享了数据。
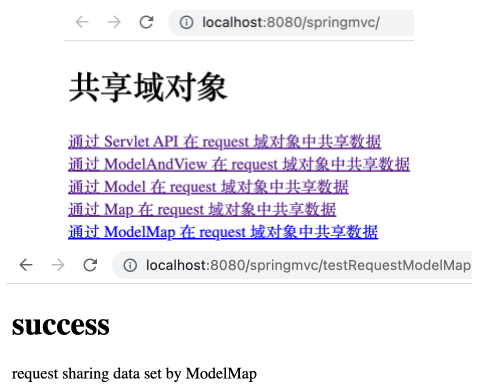
ModelMap
SpringMVC 提供了 ModelMap 类,可以在控制器方法中传入 ModelMap 实例,并利用 addAttribute 方法向 request 作用域中设置共享数据。
在 ScopeController 控制器中增加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/testRequestModelMap") public String testRequestModelMap (ModelMap modelMap) { modelMap.addAttribute("testRequestScope" , "request sharing data set by ModelMap" ); return "success" ; }
在 index.html 的 <body> 标签中加入如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testRequestModelMap}" > 通过 ModelMap 在 request 域对象中共享数据</a > <br >
运行项目,打开 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/ ,点击相应链接后可看到如下,表明通过 ModelMap 实例对象在 request 作用域下共享了数据。
小结
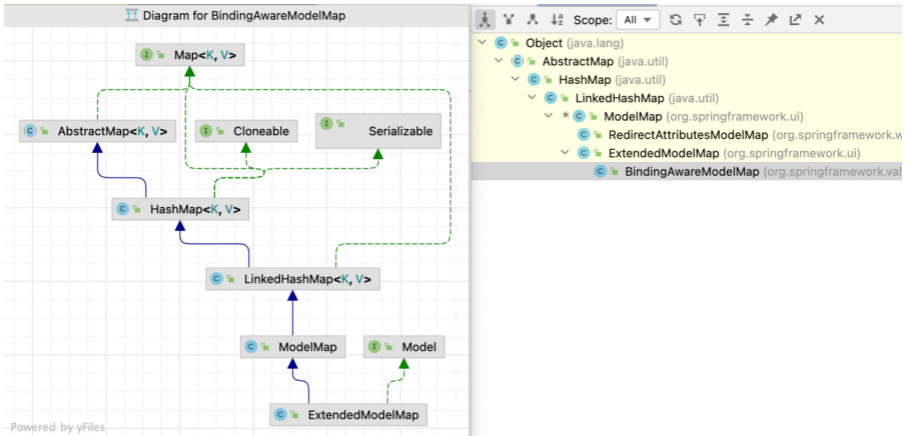
前面的示例中,Model、ModelMap、Map 类型的参数实际上都是 BindingAwareModelMap 类型的实例对象。
1 2 3 4 public interface Model{} public class ModelMap extends LinkedHashMap<String, Object> {} public class ExtendedModelMap extends ModelMap implements Model {} public class BindingAwareModelMap extends ExtendedModelMap {}
在实践中一般使用 ModelAndView 来共享 request 域数据,实际上无论使用哪一种方式,最终都会将共享数据封装到 ModelAndView 对象实例中 (更具体地,是 ModelAndView 实例中的 ModelMap 字段中)。
session域共享
将 HttpSession session 作为控制器方法的形参,此时 session 为当前会话对象,通过该对象的 setAttribute 方法共享 session 域数据。
在 ScopeController 控制器中增加如下方法。
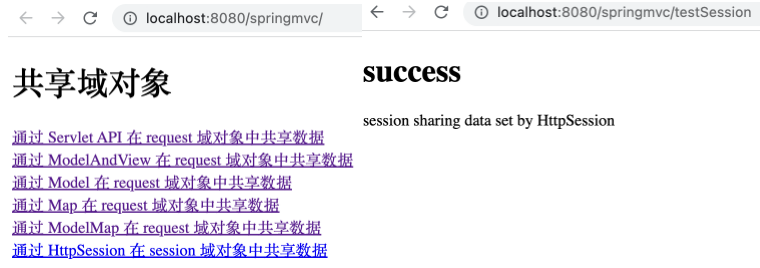
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/testSession") public String testSession (HttpSession session) { session.setAttribute("testSessionScope" , "session sharing data set by HttpSession" ); return "success" ; }
在 index.html 的 <body> 标签中加入如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testSession}" > 通过 HttpSession 在 session 域对象中共享数据</a > <br >
在 success.html 的 <body> 标签中加入如下获取 session 共享数据的 <p> 标签。
1 <p th:text ="${session.testSessionScope}" > </p >
运行项目,打开 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/ ,点击相应链接后可看到如下,表明通过 HttpSession 实例对象在 session 作用域下共享了数据。
application域共享
将 HttpSession session 或 HttpServletRequest request 作为控制器方法的形参,通过 session 或 request 的 getServletContext() 方法获取 ServletContext application 。此时 application 为当前应用上下文对象,通过该对象的 setAttribute 方法共享 application 域数据。
在 ScopeController 控制器中增加如下方法。
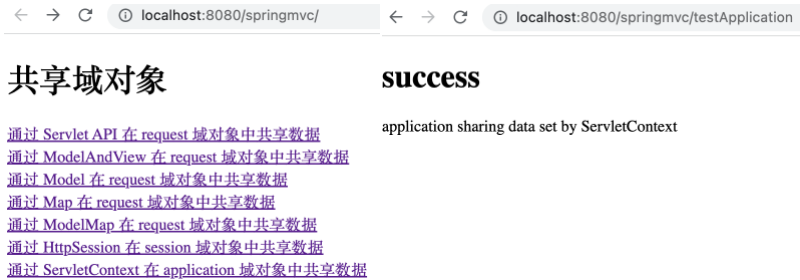
1 2 3 4 5 6 @RequestMapping("/testApplication") public String testApplication (HttpSession session) { ServletContext application = session.getServletContext(); application.setAttribute("testApplicationScope" , "application sharing data set by ServletContext" ); return "success" ; }
上述方法通过 HttpSession 对象来获取 ServletContext 对象,也可以通过 HttpServletRequest 对象来获取。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @RequestMapping("/testApplication") public String testApplication (HttpServletRequest request) { ServletContext application = request.getServletContext(); application.setAttribute("testApplicationScope" , "application sharing data set by ServletContext" ); return "success" ; }
在 index.html 的 <body> 标签中加入如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testApplication}" > 通过 ServletContext 在 application 域对象中共享数据</a > <br >
在 success.html 的 <body> 标签中加入如下获取 application 共享数据的 <p> 标签。
1 <p th:text ="${application.testApplicationScope}" > </p >
运行项目,打开 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/ ,点击相应链接后可看到如下,表明通过 ServletContext 实例对象在 application 作用域下共享了数据。
视图
SpringMVC 中的视图是 View 接口,视图的作用是渲染数据,即将模型 Model 中的数据展示给用户。
SpringMVC 有很多种视图,默认有转发视图和重定向视图。若使用的视图技术为 Thymeleaf,则需要在 SpringMVC 的配置文件中配置 Thymeleaf 的视图解析器,由此视图解析器解析之后所得到的是 ThymeleafView。
复制之前的 springmvc-demo3 为 springmvc-demo4 子项目。在父项目的 <modules> 标签中加入该子项目,并调整项目下的文件后如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 springmvc-demo4 ├── pom.xml └── src └── main ├── java │ └── com │ └── yukiyama │ └── mvc │ └── controller │ ├── TestController.java │ └── ViewController.java ├── resources │ └── springMVC.xml └── webapp └── WEB-INF ├── templates │ ├── success.html │ └── test_view.html └── web.xml
其中 ViewController 控制器、test_view.html 、success.html 均为新建 (html 要引入 thymeleaf 命名空间),用于完成后续演示。
TestController.java 改为如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package com.yukiyama.mvc.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@Controller public class TestController { @RequestMapping("/view") public String testView () { return "test_view" ; } }
ViewController.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package com.yukiyama.mvc.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@Controller public class ViewController { @RequestMapping("/testThymeleafView") public String testThymeleafView () { return "success" ; } }
test_view.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thyemleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > </head > <body > <h1 > 测试视图</h1 > </body > </html >
success.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thyemleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > </title > </head > <body > <h1 > success</h1 > </body > </html >
后续在 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/view 页面中通过点击不同链接,结合断点调试分析源码完观察不同视图的使用原理。
ThymeleafView
当控制器方法中所设置的 视图名称无前缀时 (前缀指的是转发前缀 forward: 和重定向前缀 redirect: ) ,视图名称会被 SpringMVC 配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析得到相应的视图 (例如使用 Thymeleaf 时将得到 ThymeleafView 视图) 。视图名称拼接视图前缀和视图后缀所得到的最终路径,并通过 转发的方式 实现跳转。以下在源码层面观察使用该视图时的情形。
在 ViewController 控制器中增加如下方法。
在 return "success"; 处设置断点,后续我们将深入源码观察无前缀的视图名称是如何获得 ThymeleafView 的。
1 2 3 4 @RequestMapping("/testThymeleafView") public String testThymeleafView () { return "success" ; }
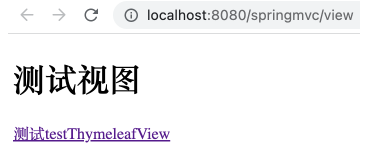
在 test_view.html 的 <body> 标签中加入如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testThymeleafView}" > 测试testThymeleafView</a > <br >
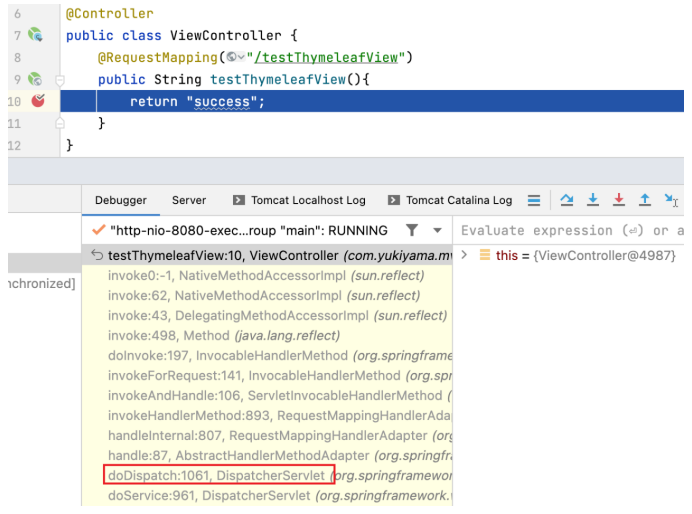
运行项目,打开 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/view ,点击相应链接后程序运行至断点处。
在 Debug 页签的方法栈中找到 doDispatch 方法,点击进入该方法。
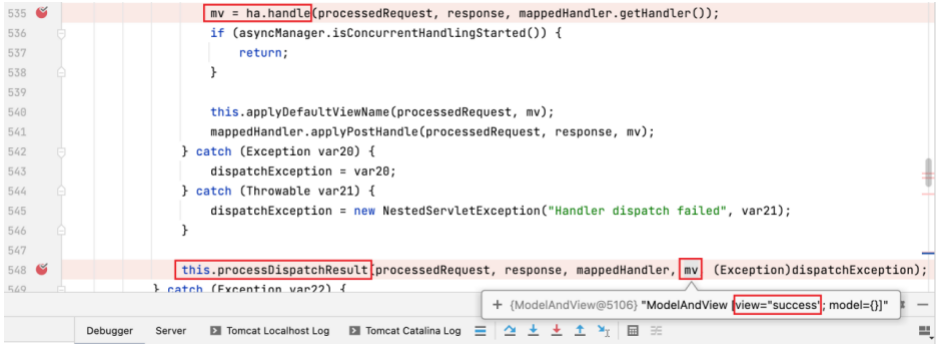
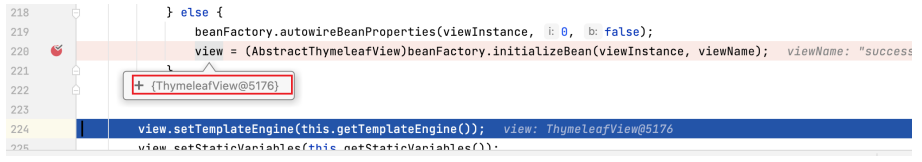
进入后位于如下 mv = ha.handle 行,mv 即 ModelAndView 实例,此实例将作为下方 processDispatchResult 方法的入参,而且可以看到作为参数时 mv 实例已经得到了正确的 view (即 "success" )。见名知义, processDispatchResult 方法用于处理转发结果。
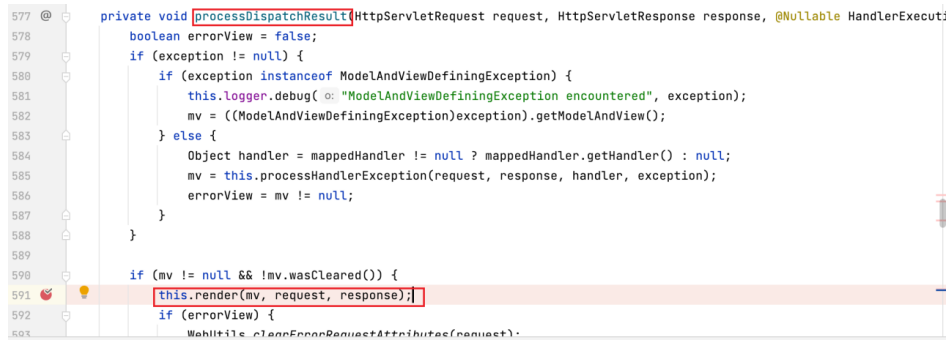
打上断点进入该方法,为其中的渲染方法 render 打上断点。
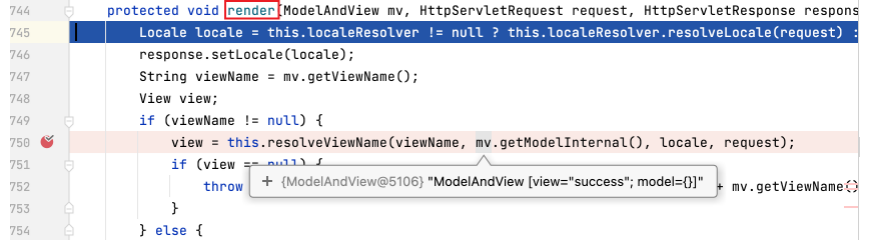
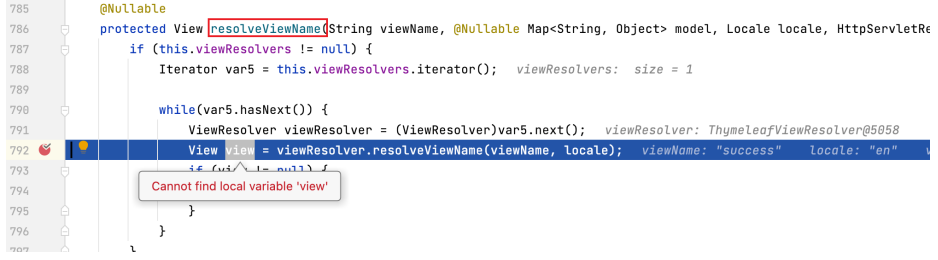
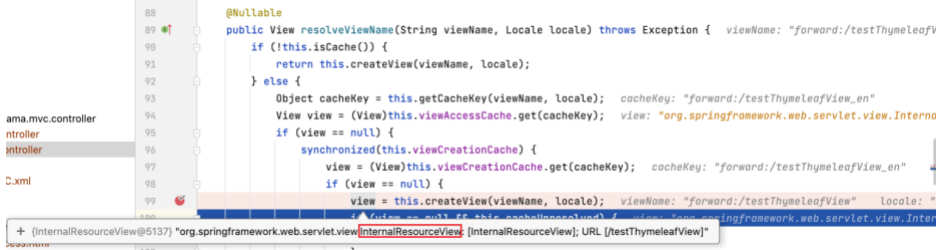
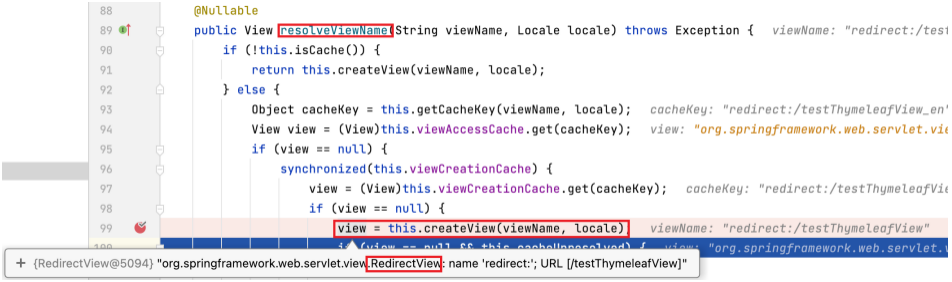
可以看到,render 方法中执行 resolveViewName ,通过传入的 viewName (即 "success" ) 来取得 view 实例。
为 resolveViewName 方法打上断点,进入该方法后可以看到,view 是通过另一个同名方法 resolveViewName 的执行而取得的。
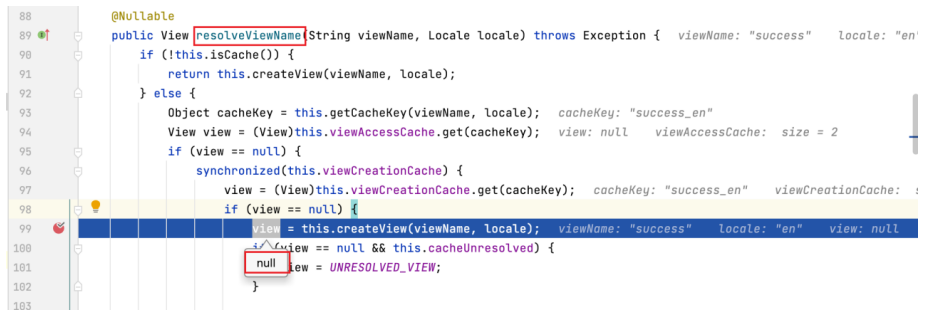
继续为此 resolveViewName 打上断点,进入该方法。
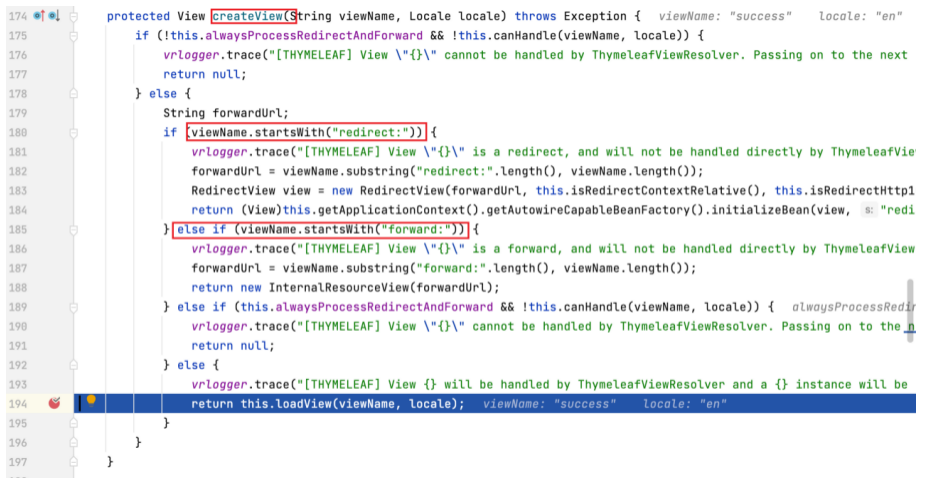
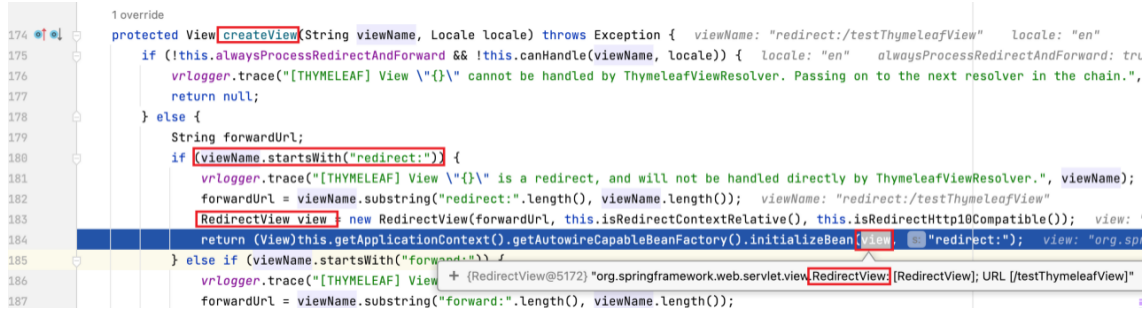
为 createView 方法打上断点,进入该方法。可以看到该方法会检查视图名称是否有 redirect: 或 forward: 前缀,当前视图名称无前缀,方法执行到 loadView 行。
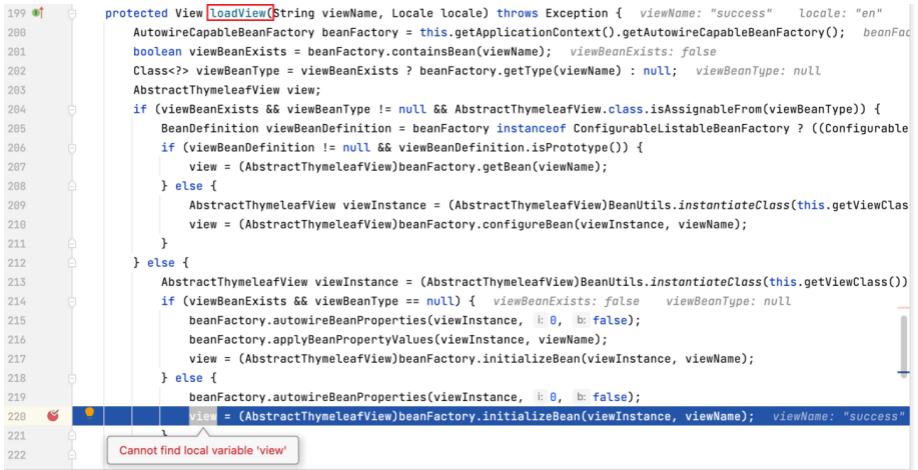
为 loadView 方法打上断点,进入该方法。
该方法指定到 (AbstractThymeleafView) beanFactory.initializeBean 一行时,view 还未取得值,当该行执行结束时,view 最终取得值,为 ThymeleafView 。
InternalResourceView
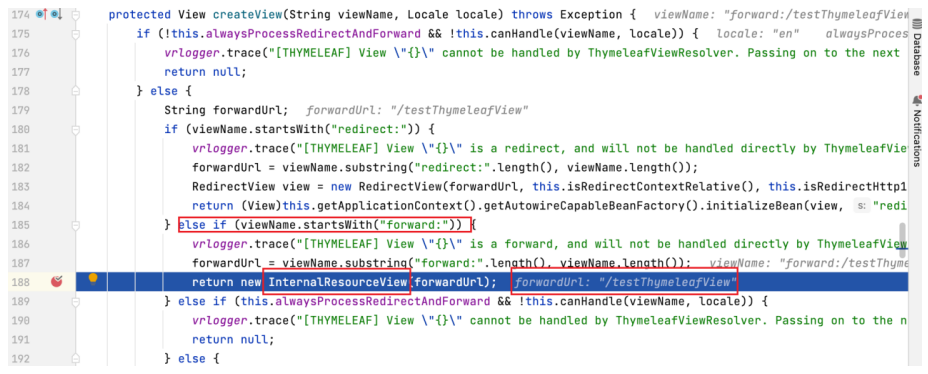
SpringMVC 中默认的 转发视图 是 InternalResourceView 。当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称以 forward: 为前缀时,视图名称不会被 SpringMVC 配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,而是会将前缀 forward: 去掉,剩余部分作为最终路径通过 转发的方式 实现跳转。相应的视图为 InternalResourceView 视图。
在 ViewController 控制器中增加如下方法。
在 return 处设置断点,后续我们将深入源码观察 forward: 视图名称是如何获得 InternalResourceView 的。
1 2 3 4 @RequestMapping("/testForward") public String testForward () { return "forward:/testThymeleafView" ; }
在 test_view.html 的 <body> 标签中加入如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testForward}" > 测试转发视图</a > <br >
运行项目,打开 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/view ,点击相应链接后程序运行至断点处。
在 Debug 页签的方法栈中找到 doDispatch 方法,点击进入该方法。从此步骤开始一直进入到 createView 方法前,与「ThymeleafView」 一节的分析过程相同。
进入到 createView 方法后,可以看到由于视图名称有 forward: 前缀,因此进入 viewName.startsWith("forward:") 分支,并返回 InternalResourceView 视图实例。
当 createView 方法执行结束时,view 最终取得值,为 InternalResourceView 。
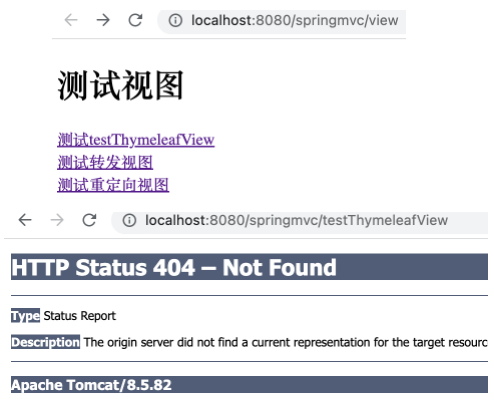
RedirectView
SpringMVC 中默认的重定向视图是 RedirectView 。当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称以 redirect: 为前缀时,创建 RedirectView 视图,此时的视图名称不会被 SpringMVC 配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,而是会将前缀 redirect: 去掉,剩余部分作为最终路径通过 重定向的方式 实现跳转。
在实际业务中,当前请求处理完成后经常需要跳转到其他相比转发视图,重定向视图更常用。
※ 重定向视图在解析时,会先将 redirect: 前缀去掉,然后会判断剩余部分是否以 / 开头,若是则会自动拼接上下文路径。
在 ViewController 控制器中增加如下方法。
在 return 处设置断点,后续我们将深入源码观察 redirect: 视图名称是如何获得 RedirectView 的。
1 2 3 4 @RequestMapping("/testRedirect") public String testRedirect () { return "redirect:/testThymeleafView" ; }
在 test_view.html 的 <body> 标签中加入如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testRedirect}" > 测试重定向视图</a > <br >
运行项目,打开 http://localhost:8080/springMVC/view ,点击相应链接后程序运行至断点处。
在 Debug 页签的方法栈中找到 doDispatch 方法,点击进入该方法。从此步骤开始一直进入到 createView 方法前,与「ThymeleafView」 一节的分析过程相同。
进入到 createView 方法后,可以看到由于视图名称有 redirect: 前缀,因此进入 viewName.startsWith("redirect:") 分支,并返回 InternalResourceView 视图实例。
当 createView 方法执行结束时,view 最终取得值,为 RedirectView 。
视图控制器
当控制器方法仅实现页面跳转而无需转发或重定向到其他页面,即只需要设置无前缀视图名称时,可在 SpringMVC 配置文件中用 <view-controller> 标签来代替以 @RequestMapping 注解的控制器方法。
注释掉如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Controller public class TestController {}
在 SpringMVC.xml 中增加 mvc 命名空间以及 view-controller 标签。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd" > <context:component-scan base-package ="com.yukiyama.mvc.controller" > </context:component-scan > <bean id ="viewResolver" class ="org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver" > <property name ="order" value ="1" /> <property name ="characterEncoding" value ="UTF-8" /> <property name ="templateEngine" > <bean class ="org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine" > <property name ="templateResolver" > <bean class ="org.thymeleaf.spring5.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver" > <property name ="prefix" value ="/WEB-INF/templates/" /> <property name ="suffix" value =".html" /> <property name ="templateMode" value ="HTML5" /> <property name ="characterEncoding" value ="UTF-8" /> </bean > </property > </bean > </property > </bean > <mvc:view-controller path ="/view" view-name ="test_view" > </mvc:view-controller > </beans >
运行项目,可以打开 http://localhost:8080/springmvc/view 页面,但点击其中的链接返回 404 错误。
出现 404 错误的原因是当 SpringMVC 中设置 <view-controller> 时,其他控制器中的请求映射将失效,在 springMVC.xml 中的 <beans> 标签内设置 mvc 注解驱动即可 ( <mvc:annotation-driven /> 标签)。
1 2 <mvc:annotation-driven />
RESTful
概念
REST:Re presentational S tate T ransfer,具体 (表述层) 状态转移。
最原始的定义可参考 Roy Thomas Fielding 于2000年发表的博士论文中 Representational State Transfer (REST) 一节的描述。
还可以参考此 视频 。
资源
资源是一种看待服务器的方式,即将服务器看作是由很多离散的资源组成。每个资源是服务器上一个可命名的抽象概念。因为资源是一个抽象的概念,所以它不仅仅能代表服务器文件系统中的一个文件、数据库中的一张表等等具体的东西,还可以将将资源理解为一些抽象事物。与面向对象设计类似,资源是以名词为核心来组织的,首先关注的是名词。一个资源可以由一个或多个 URI 来标识。URI 既是资源的名称,也是资源在 Web 上的地址。对某个资源感兴趣的客户端应用,可以通过资源的 URI 与其进行交互。
Representational State
理解了资源,再理解 Representational State 。 state 即状态,客户端与服务端的交互,本质是要改变资源的状态。例如在浏览器上点击「删除」按键删除一条记录,传递到服务器的是删除请求而非「资源」,服务器中相应的记录被删除后,可以说服务器中相应资源的状态被改变了,这就是 State 的意涵。
Representational 是一个形容词,意为 「showing things as they are normolly seen」 。例如 representational art / 具象艺术,是一种描绘现实存在的事物的绘画艺术。Representational State 即具体状态,或通常所说的「表述层状态」,通常可以理解为增/删/改/查。
transfer
即转移,转变。在客户端和服务器端之间转移代表资源状态的表述。通过转移和操作资源的表述,来间接实现操作资源的目的。
-ful
「xxx-ful」为形容词后缀,意为「充满了xxx的」、「富有xxx的」、「很有xxx的」,例如 beautiful, colorful, helpful 等。
实现
实现 RESTful ,简单来说就是以 REST 风格的 URL 完成增删改查操作,对应的 http 请求类型:GET 用来获取资源 (查),POST 用来新建资源 (增),PUT 用来更新资源 (改),DELETE 用来删除资源 (删)。
而所谓 REST 风格指 URL 中不使用问号键值对方式携带请求参数,而是将要发送给服务器的数据作为 URL 地址的一部分,均以 / 隔开。
操作
传统方式
REST风格
查询操作
getUserById?id=1
user/1 (GET 类型)
保存操作
saveUser
user (POST类型)
删除操作
deleteUser?id=1
user/1 (DELETE类型)
更新操作
updateUser
user (PUT类型)
可以明显地看到 REST 风格的 URL 可以极大地压缩 URL 的数量。可以理解为,对同一资源的操作总是使用同一个 URL,而将具体操作体现在请求类型中。
在 springmvc-demo04 中增加如下 UserController 控制器,后续在此控制器中添加用于演示 RESTful 风格的增上改查方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 package com.yukiyama.mvc.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;@Controller public class UserController {}
新建 test_rest.html 配合演示。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thymeleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > </head > <body > </body > </html >
在 springMVC.xml 中添加如下视图控制器配合演示。
1 <mvc:view-controller path ="/rest" view-name ="test_rest" > </mvc:view-controller >
查询
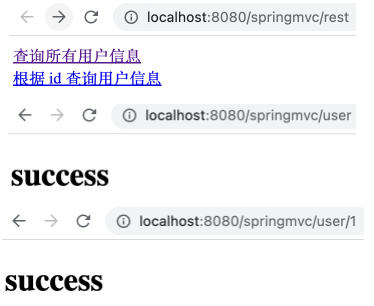
在 UserController 中添加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @RequestMapping(value = "/user", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String getAllUsers () { System.out.println("查询所有用户信息" ); return "success" ; } @RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String getUserById () { System.out.println("根据 id 查询用户信息" ); return "success" ; }
在 test_rest.html 的 <body> 标签中添加如下超链接。
1 2 <a th:href ="@{/user}" > 查询所有用户信息</a > <br > <a th:href ="@{/user/1}" > 根据 id 查询用户信息</a > <br >
运行项目,可以看到如下。同时,分别点击两条链接时,控制台输出相应的内容。
添加
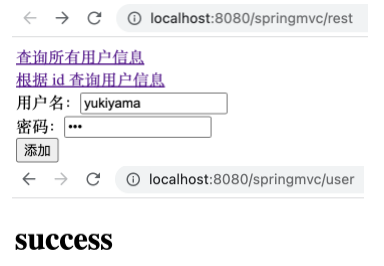
在 UserController 中添加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping(value = "/user", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String insertUser (String username, String password) { System.out.println("添加用户: " + username + ", " + password); return "success" ; }
在 test_rest.html 的 <body> 标签中添加如下表单。
1 2 3 4 5 <form th:action ="@{/user}" method ="post" > 用户名:<input type ="text" , name ="username" > <br > 密码:<input type ="password" , name ="password" > <br > <input type ="submit" , value ="添加" > <br > </form >
运行项目,在表单中填入 yukiyama, 123 可以看到如下,且控制台输出相应内容。
修改
HiddenHttpMethodFilter
浏览器只支持发送 GET 和 POST 方式的请求,而修改操作对应的是 PUT 请求,我们需要 SpringMVC 提供的 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 过滤器 将 POST 请求转换为 DELETE 或 PUT 请求 。
在 web.xml 中配置 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 过滤器。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <filter > <filter-name > HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name > <filter-class > org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class > </filter > <filter-mapping > <filter-name > HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name > <url-pattern > /*</url-pattern > </filter-mapping >
如下是 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 类中执行过滤动作的 doFilterInternal 方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public static final String DEFAULT_METHOD_PARAM = "_method" ;private String methodParam = DEFAULT_METHOD_PARAM;@Override protected void doFilterInternal (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException { HttpServletRequest requestToUse = request; if ("POST" .equals(request.getMethod()) && request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE) == null ) { String paramValue = request.getParameter(this .methodParam); if (StringUtils.hasLength(paramValue)) { String method = paramValue.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH); if (ALLOWED_METHODS.contains(method)) { requestToUse = new HttpMethodRequestWrapper (request, method); } } } filterChain.doFilter(requestToUse, response); }
HttpMethodRequestWrapper 内部类。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 private static class HttpMethodRequestWrapper extends HttpServletRequestWrapper { private final String method; public HttpMethodRequestWrapper (HttpServletRequest request, String method) { super (request); this .method = method; } @Override public String getMethod () { return this .method; } }
可以看到,HiddenHttpMethodFilter 处理 PUT / DELETE 请求的条件如下。
当前请求的请求方式必须为 POST 。
当前请求必须传输请求参数 _method 。
满足以上条件,HiddenHttpMethodFilter 过滤器就会将当前请求的请求方式转换为请求参数 _method 的值,因此请求参数 _method 的值才是最终的请求方式。
※ 目前为止,SpringMVC 中提供了两个过滤器:CharacterEncodingFilter 和 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 。在 web.xml 中注册时,必须先注册 CharacterEncodingFilter ,再注册 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 。这是因为在 CharacterEncodingFilter 中通过 request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding) 方法设置字符集之前不能有获取请求参数的操作,而 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 恰有一个获取请求方式的操作:
1 String paramValue = request.getParameter(this .methodParam);
设置过滤器后,按如下完成 RESTful 风格的修改。
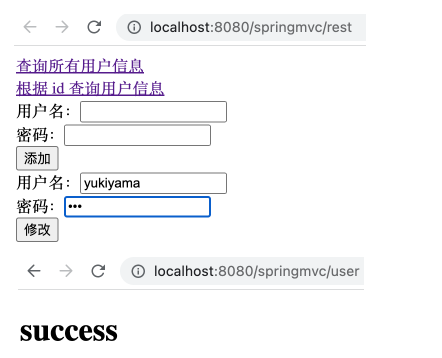
在 UserController 中添加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping(value = "/user", method = RequestMethod.PUT) public String updateUser (String username, String password) { System.out.println("修改用户: " + username + ", " + password); return "success" ; }
在 test_rest.html 的 <body> 标签中添加如下表单。
1 2 3 4 5 6 <form th:action ="@{/user}" method ="post" > <input type ="hidden" name ="_method" value ="PUT" > 用户名:<input type ="text" , name ="username" > <br > 密码:<input type ="password" , name ="password" > <br > <input type ="submit" , value ="修改" > <br > </form >
运行项目,可以看到如下。在表单中填入 yukiyama, 456 可以看到如下,且控制台输出相应内容。
删除
在 UserController 中添加如下方法。
在 test_rest.html 的 <body> 标签中添加如下超链接。
运行项目,可以看到如下。
案例
准备工作
新建 springmvc-rest 子工程用于演示 RESTful 风格的增删改查。
该子工程目录结构如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 springmvc-rest ├── pom.xml └── src └── main ├── java │ └── com │ └── yukiyama │ └── rest │ ├── beans │ │ └── Employee.java │ ├── controller │ │ └── EmployeeController.java │ └── dao │ └── EmployeeDao.java ├── resources │ └── springMVC.xml └── webapp └── WEB-INF ├── templates │ ├── employee_list.html │ └── index.html └── web.xml
springMVC.xml 与 web.xml 与之前的设置类似,其他文件如下。
Employee.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 package com.yukiyama.rest.beans;public class Employee { private Integer id; private String lastName; private String email; private Integer gender; public Employee () { } public Employee (Integer id, String lastName, String email, Integer gender) { super (); this .id = id; this .lastName = lastName; this .email = email; this .gender = gender; } public Integer getId () { return id; } public void setId (Integer id) { this .id = id; } public String getLastName () { return lastName; } public void setLastName (String lastName) { this .lastName = lastName; } public String getEmail () { return email; } public void setEmail (String email) { this .email = email; } public Integer getGender () { return gender; } public void setGender (Integer gender) { this .gender = gender; } }
EmployeeController.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 package com.yukiyama.rest.controller;import com.yukiyama.rest.beans.Employee;import com.yukiyama.rest.dao.EmployeeDao;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.ui.Model;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;import java.util.Collection;@Controller public class EmployeeController { @Autowired private EmployeeDao employeeDao; }
EmployeeDao.java
并不实际连接数据库,而是以静态数据模拟。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 package com.yukiyama.rest.dao;import java.util.Collection;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;import com.yukiyama.rest.beans.Employee;import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;@Repository public class EmployeeDao { private static Map<Integer, Employee> employees = null ; static { employees = new HashMap <Integer, Employee>(); employees.put(1001 , new Employee (1001 , "E-AA" , "aa@163.com" , 1 )); employees.put(1002 , new Employee (1002 , "E-BB" , "bb@163.com" , 1 )); employees.put(1003 , new Employee (1003 , "E-CC" , "cc@163.com" , 0 )); employees.put(1004 , new Employee (1004 , "E-DD" , "dd@163.com" , 0 )); employees.put(1005 , new Employee (1005 , "E-EE" , "ee@163.com" , 1 )); } private static Integer initId = 1006 ; public void save (Employee employee) { if (employee.getId() == null ){ employee.setId(initId++); } employees.put(employee.getId(), employee); } public Collection<Employee> getAll () { return employees.values(); } public Employee get (Integer id) { return employees.get(id); } public void delete (Integer id) { employees.remove(id); } }
index.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 首页</title > </head > <body > <h1 > 首页</h1 > </body > </html >
本案例将实现如下功能。
功能
URL 地址
请求方式
访问首页
/
GET
查询全部数据
/employee
GET
删除
/employee/2
DELETE
跳转到添加数据页面
/toAdd
GET
执行保存
/employee
POST
跳转到更新数据页面
/employee/2
GET
执行更新
/employee
PUT
查询所有
在 EmployeeController 控制器中添加如下方法。
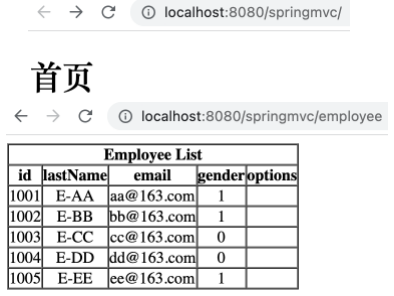
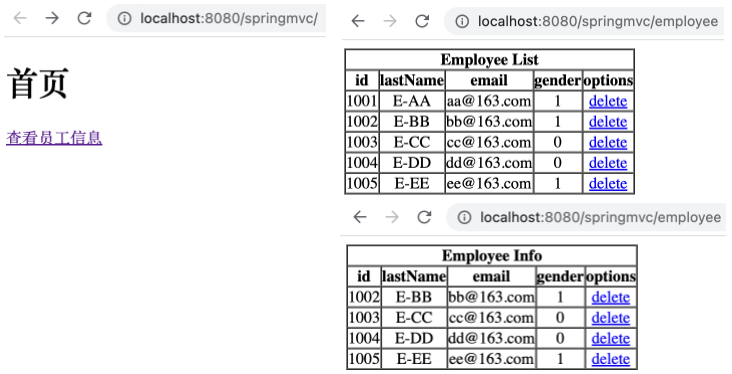
1 2 3 4 5 6 @RequestMapping(value = "/employee", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String getAllEmployee (Model model) { Collection<Employee> employeeList = employeeDao.getAll(); model.addAttribute("employeeList" , employeeList); return "employee_list" ; }
新增显示所有员工信息的页面 employee_list.html ,如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Employee List</title > </head > <body > <table border ="1" cellspacing ="0" cellpadding ="0" style ="text-align: center" > <tr > <th colspan ="5" > Employee List</th > </tr > <tr > <th > id</th > <th > lastName</th > <th > email</th > <th > gender</th > <th > options</th > </tr > <tr th:each ="employee : ${employeeList}" > <td th:text ="${employee.id}" > </td > <td th:text ="${employee.lastName}" > </td > <td th:text ="${employee.email}" > </td > <td th:text ="${employee.gender}" > </td > <td > <a href ="delete" > </a > <a href ="update" > </a > </td > </tr > </table > </body > </html >
在 index.html 中添加跳转到 employee_list.html 页面的超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/employee}" > 查看员工信息</a >
将该子工程部署到 Tomcat 中,运行该子工程,打开「首页」后,点击链接可以看到员工信息表。
删除
删除操作超链接绑定点击事件,通过点击删除操作超链接完成删除。如下是在 employee_list.html 中添加的内容。
引入 vue.js
1 <script type ="text/javascript" th:src ="@{/static/js/vue.js}" > </script >
删除操作超链接
1 2 3 <td > <a @click ="deleteEmployee" th:href ="@{'/employee/'+${employee.id}}" > delete</a > </td >
通过 vue 处理点击事件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <script type ="text/javascript" > var vue = new Vue ({ el :"#dataTable" , methods :{ deleteEmployee :function (event ) { var deleteForm = document .getElementById ("deleteForm" ); deleteForm.action = event.target .href ; deleteForm.submit (); event.preventDefault (); } } }); </script >
在 EmployeeController 控制器中添加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping(value = "/employee/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE) public String deleteEmployee (@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { employeeDao.delete(id); return "redirect:/employee" ; }
运行工程,可以通过点击 delete 超链接删除相应的员工信息。
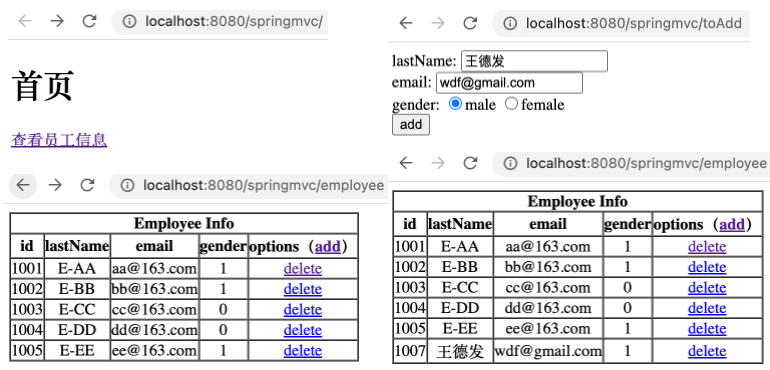
添加
新建添加用户信息页面 employee_add.html 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > add employee</title > </head > <body > <form th:action ="@{/employee}" method ="post" > lastName: <input type ="text" name ="lastName" > <br > email: <input type ="text" name ="email" > <br > gender: <input type ="radio" name ="gender" value ="1" > male <input type ="radio" name ="gender" value ="0" > female<br > <input type ="submit" value ="add" > <br > </form > </body > </html >
在 employee_list.html 中添加 toAdd 超链接。
1 <th > options(<a th:href ="@{/toAdd}" > add</a > )</th >
在 springMVC.xml 中添加如下视图控制器。
1 <mvc:view-controller path ="/toAdd" view-name ="employee_add" > </mvc:view-controller >
在 EmployeeController 控制器中添加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping(value = "/employee", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String addEmployee (Employee employee) { employeeDao.save(employee); return "redirect:/employee" ; }
运行工程,如下,可以通过 options 后的 add 超链接跳转到添加用户的页面,可成功添加。
更新
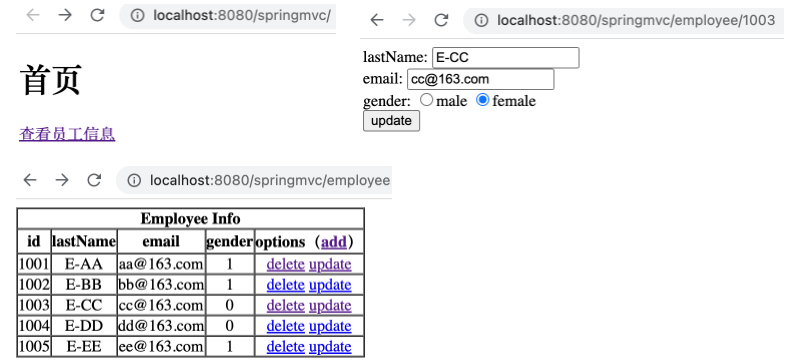
新建更新用户信息页面 employee_update.html 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > update employee</title > </head > <body > <form th:action ="@{/employee}" method ="post" > <input type ="hidden" name ="_method" value ="put" > <input type ="hidden" name ="id" th:value ="${employee.id}" > lastName: <input type ="text" name ="lastName" th:value ="${employee.lastName}" > <br > email: <input type ="text" name ="email" th:value ="${employee.email}" > <br > gender: <input type ="radio" name ="gender" value ="1" th:field ="${employee.gender}" > male <input type ="radio" name ="gender" value ="0" th:field ="${employee.gender}" > female<br > <input type ="submit" value ="update" > <br > </form > </body > </html >
在 employee_list.html 中添加 update 超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{'/employee/'+${employee.id}}" > update</a >
在 EmployeeController 控制器中添加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @RequestMapping(value = "/employee/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String getEmployeeById (@PathVariable("id") Integer id, Model model) { Employee employee = employeeDao.get(id); model.addAttribute("employee" , employee); return "employee_update" ; }
运行工程,如下,可以通过 update 超链接跳转到更新用户信息的页面。
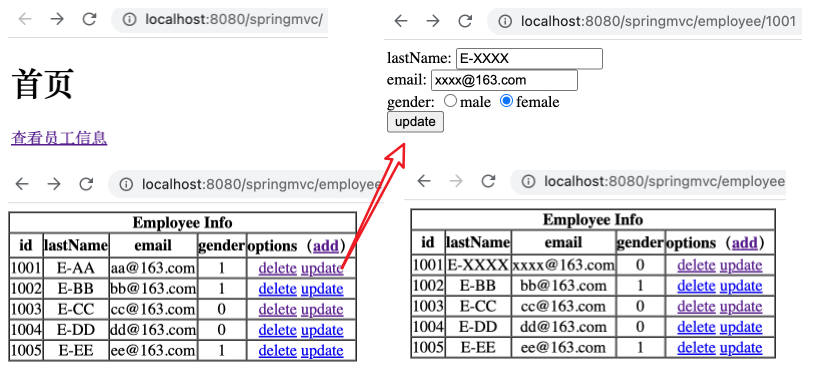
接着在 EmployeeController 控制器中添加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping(value = "/employee", method = RequestMethod.PUT) public String updateEmployee (Employee employee) { employeeDao.save(employee); return "redirect:/employee" ; }
运行工程,如下,可以通过 update 超链接跳转到更新用户信息的页面,更新信息后重定向回到员工信息页面。
HttpMessageConverter
HttpMessageConverter,报文信息转换器,它提供了两个注解和两个类型,可将请求报文转换为 Java 对象,或将 Java 对象转换为响应报文。
注解或类型
描述
@RequestBody参数注解,用以获取请求体。
RequestEntity类型,用以获取请求报文。
@ResponseBody注解参数,用以获取响应体。
ResponseEntity类型,用以获取相应报文。
新建 springmvc-demo5 子工程用于演示本节内容。该工程目录结构和主要文件内容如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 springmvc-demo5 ├── pom.xml └── src └── main ├── java │ └── com │ └── yukiyama │ └── mvc │ └── controllers │ └── HttpController.java ├── resources │ └── springMVC.xml └── webapp └── WEB-INF ├── templates │ ├── index.html │ └── success.html └── web.xml
HttpController 控制器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 package com.yukiyama.mvc.controllers;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;@Controller public class HttpController {}
index.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 首页</title > </head > <body > <h1 > 首页</h1 > </body > </html >
success.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > success</title > </head > <body > <h1 > success</h1 > </body > </html >
@RequestBody
使用 @RequestBody 标识控制器方法形参,当前请求的请求体就会为当前注解所标识的形参赋值。
在 index.html 页面中添加如下表单,确保发起请求时请求体不为空。
1 2 3 4 5 <form th:action ="@{/testRequestBody}" method ="post" > <input type ="text" name ="username" > <br > <input type ="text" name ="password" > <br > <input type ="submit" value ="测试@RequestBody" > </form >
在 HttpController 控制器中添加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/testRequestBody") public String testRequestBody (@RequestBody String requestBody) { System.out.println("requestBody = " + requestBody); return "success" ; }
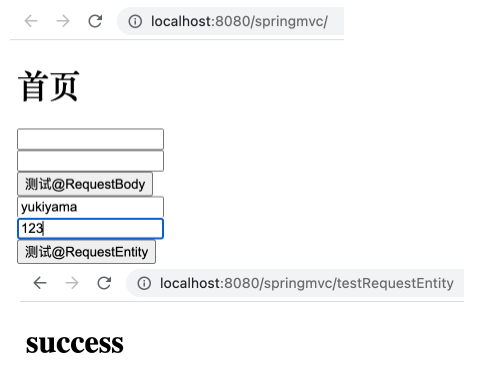
运行工程,如下,添入内容后,控制器方法中的打印语句在控制台中打印出了 requestBody = username=yukiyama&password=123 请求体内容。
RequestEntity
RequestEntity 封装请求报文的一种类型,在控制器方法的形参中设置该类型的形参,当前请求的请求报文就会赋值给该形参,可以通过 getHeaders() 获取请求头信息,通过 getBody() 获取请求体信息。
在 index.html 页面中添加如下表单,确保发起请求时请求体不为空。
1 2 3 4 5 <form th:action ="@{/testRequestEntity}" method ="post" > <input type ="text" name ="username" > <br > <input type ="text" name ="password" > <br > <input type ="submit" value ="测试@RequestEntity" > </form >
在 HttpController 控制器中添加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @RequestMapping("/testRequestEntity") public String testRequestEntity (RequestEntity<String> requestEntity) { System.out.println("requestEntity headers = " + requestEntity.getHeaders()); System.out.println("requestEntity body = " + requestEntity.getBody()); return "success" ; }
运行工程,如下。
控制台输出结果
1 2 requestEntity headers = [host:"localhost:8080", connection:"keep-alive", content-length:"30", cache-control:"max-age=0", sec-ch-ua:""Google Chrome";v="107", "Chromium";v="107", "Not=A?Brand";v="24"", sec-ch-ua-mobile:"?0", sec-ch-ua-platform:""macOS"", upgrade-insecure-requests:"1", origin:"http://localhost:8080", user-agent:"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/107.0.0.0 Safari/537.36", accept:"text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9", sec-fetch-site:"same-origin", sec-fetch-mode:"navigate", sec-fetch-user:"?1", sec-fetch-dest:"document", referer:"http://localhost:8080/springmvc/", accept-encoding:"gzip, deflate, br", accept-language:"en,zh-CN;q=0.9,zh;q=0.8,ko-KR;q=0.7,ko;q=0.6,ja;q=0.5", cookie:"Idea-a8cf3385=05276e99-fa7c-4015-b476-2565fefd4c05", Content-Type:"application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8"] requestEntity body = username=yukiyama&password=123
@ResponseBody
@ResponseBody 为方法注解,标识控制器方法,可以将该方法的返回值作为响应报文的响应体。
先给出利用 HttpServletResponse 的方式。
在 HttpController 控制器中增加如下方法。
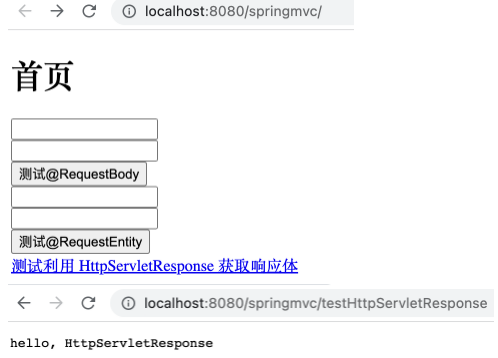
1 2 3 4 @RequestMapping("testHttpServletResponse") public void testHttpServletResponse (HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws IOException { httpServletResponse.getWriter().print("hello, HttpServletResponse" ); }
在 index.html 中添加如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testHttpServletResponse}" > 测试利用 HttpServletResponse 获取响应体</a >
运行工程,如下。
接着是利用 @ResponseBody 的方式。
在 HttpController 控制器中增加如下方法。
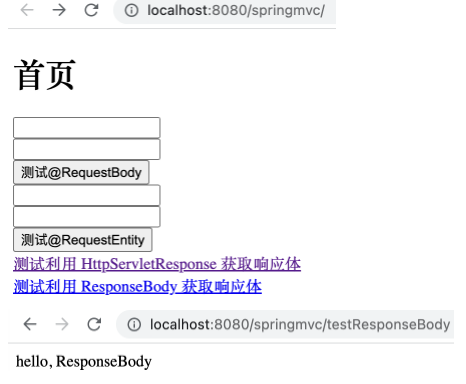
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/testResponseBody") @ResponseBody public String testResponseBody () { return "hello, ResponseBody" ; }
在 index.html 中添加如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testResponseBody}" > 测试利用 ResponseBody 获取响应体</a > <br >
运行工程,如下。
除了将 String 类型作为响应体,还可以直接返回 Java 对象,借助 jackson 的处理,将 Java 对象封装为 Json 对象作为响应体。
SpringMVC处理Json
首先要引入 jackson 依赖用以处理 Json。
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId > <artifactId > jackson-databind</artifactId > <version > 2.12.1</version > </dependency >
在 springMVC.xml 中开启 mvc 的注解驱动,此时在 HandlerAdaptor 中会自动装配一个消息转换器:MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter,可以将响应到浏览器的 Java 对象转换为 Json 格式的字符串。
1 <mvc:annotation-driven />
增加 User 类。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 package com.yukiyama.mvc.beans;public class User { private Integer id; private String username; private String password; private Integer age; private String gender; public User () { } public User (Integer id, String username, String password, Integer age, String gender) { this .id = id; this .username = username; this .password = password; this .age = age; this .gender = gender; } public Integer getId () { return id; } public void setId (Integer id) { this .id = id; } public String getUsername () { return username; } public void setUsername (String username) { this .username = username; } public String getPassword () { return password; } public void setPassword (String password) { this .password = password; } public Integer getAge () { return age; } public void setAge (Integer age) { this .age = age; } public String getGender () { return gender; } public void setGender (String gender) { this .gender = gender; } }
在 HttpController 控制器中增加如下方法。
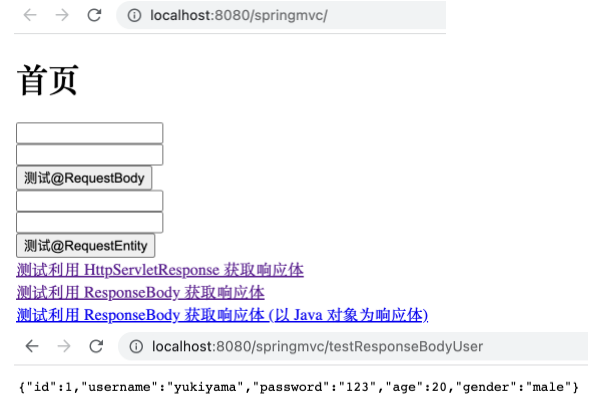
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/testResponseBodyUser") @ResponseBody public User testResponseBodyUser () { return new User (1 , "yukiyama" , "123" , 20 , "male" ); }
在 index.html 中添加如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testResponseBodyUser}" > 测试利用 ResponseBody 获取响应体 (以 Java 对象为响应体)</a > <br >
运行工程,如下。
SpringMVC处理ajax
引入 vue.js 以及 axios.min.js 文件,在 index.html 中添加如下内容。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 <div id ="app" > <a th:href ="@{/testAjax}" @click ="testAjax" > testAjax</a > <br > </div > <script type ="text/javascript" th:src ="@{/static/js/vue.js}" > </script > <script type ="text/javascript" th:src ="@{/static/js/axios.min.js}" > </script > <script type ="text/javascript" > var vue = new Vue ({ el :"#app" , methods :{ testAjax :function (event ) { axios ({ method :"post" , url :event.target .href , params :{ username :"admin" , password :"123456" } }).then (function (response ) { alert (response.data ); }); event.preventDefault (); } } }); </script >
在 HttpController 控制器中添加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @RequestMapping("/testAxios") @ResponseBody public String testAxios (String usename, String password) { System.out.println("usename = " + usename + ", password" + password); return "hello, axios" ; }
@RestController注解
@RestController 注解是 springMVC 提供的复合注解,标识在控制器的类上,就相当于为类添加了@Controller 注解,并且为其中的每个方法添加@ResponseBody 注解。
ResponseEntity
ResponseEntity 用于控制器方法的返回值类型,该控制器方法的返回值就是响应到浏览器的响应报文。
本节仍在 springmvc-demo5 工程中演示利用 ResponseEntity 实现文件上传下载功能。
新建 FileUpDownController 控制器。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 package com.yukiyama.mvc.controllers;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;@Controller public class FileUpDownController {}
新建 file.html 页面用于测试上传下载功能。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 测试文件上传和下载</title > </head > <body > <h1 > file</h1 > </body > </html >
文件下载
使用 ResponseEntity 实现下载文件的功能。
在 springMVC.xml 文件中添加如下视图控制器。
1 <mvc:view-controller path ="/file" view-name ="file" > </mvc:view-controller >
在 FileUpDownController 控制器中添加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @RequestMapping("/testDown") public ResponseEntity<byte []> testResponseEntity(HttpSession session) throws IOException { ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext(); String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath("/static/img/1.jpg" ); InputStream is = new FileInputStream (realPath); byte [] bytes = new byte [is.available()]; is.read(bytes); MultiValueMap<String, String> headers = new HttpHeaders (); headers.add("Content-Disposition" , "attachment;filename=1.jpg" ); HttpStatus statusCode = HttpStatus.OK; ResponseEntity<byte []> responseEntity = new ResponseEntity <>(bytes, headers, statusCode); is.close(); return responseEntity; }
在 file.html 中添加如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testDown}" > 下载 doraemon.png</a >
在 工程的 webapp/static/img 路径下存有 doraemon.png 文件。
运行工程,点击链接后可下载图片。
文件上传
文件上传要通过 form 表单,请求方式必须为 POST,并且需要添加属性 enctype="multipart/form-data" 。
SpringMVC 中将上传的文件封装到 MultipartFile 对象中,通过此对象可以获取文件相关信息。
上传需要用到 commons-fileupload 依赖。
1 2 3 4 5 6 <dependency > <groupId > commons-fileupload</groupId > <artifactId > commons-fileupload</artifactId > <version > 1.3.1</version > </dependency >
在 SpringMVC.xml 中添加 multipartResolver bean。
1 2 <bean id ="multipartResolver" class ="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver" > </bean >
在 FileUpDownController 控制器中添加如下方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 @RequestMapping("/testUp") public String testUp (MultipartFile photo, HttpSession session) throws IOException { String fileName = photo.getOriginalFilename(); ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext(); String photoPath = servletContext.getRealPath("photo" ); File file = new File (photoPath); if (!file.exists()){ file.mkdir(); } String finalPath = photoPath + File.separator + fileName; photo.transferTo(new File (finalPath)); return "success" ; }
在 file.html 页面中添加如下表单。
1 2 3 4 <form th:action ="@{/testUp}" method ="post" enctype ="multipart/form-data" > 文件上传:<input type ="file" name ="photo" > <br > <input type ="submit" value ="上传" > </form >
运行工程,可成功上传文件。
此外,对于同名文件,还可以在控制器方法中加入 UUID 生成语句来支持上传同名文件 (上传到服务器后文件名为 UUID) 。
支持同名文件上传的 testUp 方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @RequestMapping("/testUp") public String testUp (MultipartFile photo, HttpSession session) throws IOException { String fileName = photo.getOriginalFilename(); String hzName = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("." )); fileName = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + hzName; ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext(); String photoPath = servletContext.getRealPath("photo" ); File file = new File (photoPath); if (!file.exists()){ file.mkdir(); } String finalPath = photoPath + File.separator + fileName; photo.transferTo(new File (finalPath)); return "success" ; }
运行工程,上传效果如下。
拦截器
SpringMVC 中的拦截器用于拦截控制器方法的执行。拦截器需要实现 HandlerInterceptor 接口,此接口有三个 default 方法可供重写。
default 方法
描述
default boolean preHandle在控制器方法执行之前执行,返回 true 调用控制器方法,返回 false 表示不调用控制器方法。
default void postHandle在控制器方法执行之后执行。
default void afterCompletion在视图渲染之后执行。
示例
创建 springmvc-demo6 子工程用于演示如何使用拦截器,该工程目录及文件结构如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 springmvc-demo6 ├── pom.xml └── src └── main ├── java │ └── com │ └── yukiyama │ └── mvc │ ├── controllers │ │ └── TestController.java │ └── interceptors │ └── FirstInterceptor.java ├── resources │ └── springMVC.xml └── webapp └── WEB-INF ├── templates │ ├── index.html │ └── success.html └── web.xml
拦截器 FirstInterceptor 要实现 HandlerInterceptor。
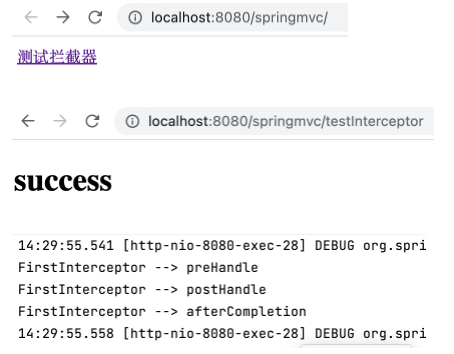
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 package com.yukiyama.mvc.interceptors;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;@Component public class FirstInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("FirstInterceptor --> preHandle" ); return true ; } @Override public void postHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { System.out.println("FirstInterceptor --> postHandle" ); } @Override public void afterCompletion (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { System.out.println("FirstInterceptor --> afterCompletion" ); }
TestController 控制器。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 package com.yukiyama.mvc.controllers;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@Controller public class TestController { @RequestMapping("/testInterceptor") public String testInterceptor () { return "success" ; } }
在 SpringMVC.xml 配置拦截器,有三种方式,如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 <mvc:interceptors > <mvc:interceptor > <mvc:mapping path ="/**" /> <mvc:exclude-mapping path ="/" /> <ref bean ="firstInterceptor" > </ref > </mvc:interceptor > </mvc:interceptors >
※ 采用方式三时, <mvc:mapping> 标签中的 path=/** 标签属性表示对于所有路径的请求所对应的控制器方法,都应用指定的拦截器。若 path=/* ,则对应所有单层的路径的请求。
index.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thyemleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > success</title > </head > <body > <a th:href ="@{/testInterceptor}" > 测试拦截器</a > <br > </body > </html >
运行工程,如下。
多个拦截器
若每个拦截器的 preHandle() 都返回 true,此时多个拦截器的执行顺序和拦截器在 SpringMVC 的配置文件的配置顺序有关。preHandle() 会按照配置的顺序执行,而 postHandle() 和 afterComplation() 会按照配置的反序执行。
若某个拦截器的 preHandle() 返回了 false,它及之前的拦截器的 preHandle() 都会执行,postHandle() 都不执行,返回 false 的拦截器之前的拦截器的afterComplation() 会执行。
异常处理器
HandlerExceptionResolver 是 SpringMVC 提供的处理控制器方法执行过程中所出现的异常的接口,其实现类有 DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver 和 SimpleMappingExceptionResolver ,后者可自定义。
可基于配置或基于注解使用异常解析器。
基于配置
按如下方式在 springMVC.xml 中自定义,如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 <bean class ="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver" > <property name ="exceptionMappings" > <props > <prop key ="java.lang.ArithmeticException" > error</prop > </props > </property > <property name ="exceptionAttribute" value ="ex" > </property > </bean >
仍在 springmvc-demo6 中演示异常解析器的使用。
新建 error.html ,发生指定异常时跳转到该页面。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thyemleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 异常页面</title > </head > <body > 出现异常 <p th:text ="${ex}" > </p > </body > </html >
在 index.html 中添加如下超链接。
1 <a th:href ="@{/testExceptionHandler}" > 测试异常处理</a > <br >
在 TestController 控制器中添加如下方法,其中 10/0 用于模拟算术异常 java.lang.ArithmeticException。
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/testExceptionHandler") public String testExceptionHandler () { System.out.println(1 /0 ); return "success" ; }
运行工程,点击「测试异常处理」链接,如下。
基于注解
新建如下 MyExceptionHandler 异常处理器,以 @ControllerActive 类注解标识,异常处理器中以 @ExceptionHandler 标识处理器方法。Excetion ex 为捕获的异常,将其写入 model 中的请求域中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 package com.yukiyama.mvc.exceptionHandlers;import org.springframework.ui.Model;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;@ControllerAdvice public class MyExceptionHandler { @ExceptionHandler public String testException (Exception ex, Model model) { model.addAttribute("ex" , ex); return "error" ; } }
运行工程,效果与「基于配置」的方式相同。
注解方式的SpringMVC
目前为止 SpirngMVC 各功能的均基于 xml 配置文件实现,实际开发场景中常使用配置类和注解代替配置文件 (包括 SpringMVC.xml 及 web.xml) 。
web.xml配置类
在 Servlet 3.0 环境中,容器会在类路径中查找实现 javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer 接口的类,如果找到的话就用它来配置 servlet 容器。Spring 提供了这个接口的实现,名为 SpringServletContainerInitializer ,这个类反过来又会查找实现 WebApplicationInitializer 的类并将配置的任务交给它们来完成。
Spring3.2 引入了一个便利的 WebApplicationInitializer 基础实现,名为 AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer ,当我们的类继承了 AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer 并将其部署到 Servlet 3.0 容器的时候,容器会自动发现它,并用它来配置 Servlet 上下文。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 package com.yukiyama.mvc.config;import org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter;import org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter;import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;import javax.servlet.Filter;public class WebInit extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer { @Override protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() { return new Class []{SpringConfig.class}; } @Override protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() { return new Class []{WebConfig.class}; } @Override protected String[] getServletMappings() { return new String []{"/" }; } @Override protected Filter[] getServletFilters() { CharacterEncodingFilter encodingFilter = new CharacterEncodingFilter (); encodingFilter.setEncoding("UTF-8" ); encodingFilter.setForceRequestEncoding(true ); HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter (); return new Filter []{encodingFilter, hiddenHttpMethodFilter}; } }
Spring配置类
1 2 3 4 @Configuration public class SpringConfig {}
SpringMVC配置类
代替 SpringMVC.xml 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 package com.yukiyama.mvc.config;import com.yukiyama.mvc.interceptors.FirstInterceptor;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader;import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;import org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver;import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver;import org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver;import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.*;import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver;import org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine;import org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver;import org.thymeleaf.templatemode.TemplateMode;import org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ITemplateResolver;import org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ServletContextTemplateResolver;import java.util.List;import java.util.Properties;@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.yukiyama.mvc.controllers") @EnableWebMvc public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void configureDefaultServletHandling (DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) { configurer.enable(); } @Bean public CommonsMultipartResolver multipartResolver () { return new CommonsMultipartResolver (); } @Override public void addInterceptors (InterceptorRegistry registry) { FirstInterceptor firstInterceptor = new FirstInterceptor (); registry.addInterceptor(firstInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/**" ); } @Override public void addViewControllers (ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/" ).setViewName("index" ); } @Override public void configureHandlerExceptionResolvers (List<HandlerExceptionResolver> resolvers) { SimpleMappingExceptionResolver exceptionResolver = new SimpleMappingExceptionResolver (); Properties prop = new Properties (); prop.setProperty("java.lang.ArithmeticException" , "error" ); exceptionResolver.setExceptionMappings(prop); exceptionResolver.setExceptionAttribute("ex" ); resolvers.add(exceptionResolver); } @Bean public ITemplateResolver templateResolver () { WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext(); ServletContextTemplateResolver templateResolver = new ServletContextTemplateResolver ( webApplicationContext.getServletContext()); templateResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/templates/" ); templateResolver.setSuffix(".html" ); templateResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8" ); templateResolver.setTemplateMode(TemplateMode.HTML); return templateResolver; } @Bean public SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine (ITemplateResolver templateResolver) { SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine = new SpringTemplateEngine (); templateEngine.setTemplateResolver(templateResolver); return templateEngine; } @Bean public ViewResolver viewResolver (SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine) { ThymeleafViewResolver viewResolver = new ThymeleafViewResolver (); viewResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8" ); viewResolver.setTemplateEngine(templateEngine); return viewResolver; } }
SpringMVC总结
SpringMVC常用组件
DispatcherServlet
前端控制器 ,框架提供。统一处理请求和响应,整个流程控制的中心,由它调用其它组件处理用户的请求。
HandlerMapping
处理器映射器 ,框架提供。根据请求的 url、method 等信息查找相应的控制器方法。
Handler (Controller)
处理器 ,工程师开发。在 DispatcherServlet 的控制下 Handler 处理具体请求。
HandlerAdapter
处理器适配器 ,框架提供。通过 HandlerAdapter 执行控制器方法。
ViewResolver
视图解析器 ,框架提供。进行视图解析,得到相应的视图,例如:ThymeleafView、InternalResourceView、RedirectView。
View
视图 ,框架提供,具体页面由工程师编写。将模型数据通过页面展示给用户。
DispatcherServlet初始化过程
DispatcherServlet 通过若干层继承和实现,实现了 Servlet 接口,因此遵循 Servlet 的生命周期。
初始化WebApplicationContext
所在类:org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext () { WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null ; if (this .webApplicationContext != null ) { wac = this .webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { if (cwac.getParent() == null ) { cwac.setParent(rootContext); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } if (wac == null ) { wac = findWebApplicationContext(); } if (wac == null ) { wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } if (!this .refreshEventReceived) { synchronized (this .onRefreshMonitor) { onRefresh(wac); } } if (this .publishContext) { String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); } return wac; }
创建WebApplicationContext
所在类:org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext (@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) { Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass(); if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) { throw new ApplicationContextException ( "Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" ); } ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment()); wac.setParent(parent); String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation(); if (configLocation != null ) { wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac); return wac; }
DispatcherServlet初始化策略
FrameworkServlet 创建 WebApplicationContext 后,刷新容器,调用 onRefresh(wac) ,此方法在 DispatcherServlet 中重写,调用了initStrategies(context) 方法,初始化策略,即初始化 DispatcherServlet 的各个组件。
所在类:org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 protected void initStrategies (ApplicationContext context) { initMultipartResolver(context); initLocaleResolver(context); initThemeResolver(context); initHandlerMappings(context); initHandlerAdapters(context); initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); initViewResolvers(context); initFlashMapManager(context); }
DispatcherServlet处理请求
processRequest()
FrameworkServlet 重写 HttpServlet 中的 service() 和 doXxx() ,这些方法中调用了processRequest(request, response) 。
所在类:org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 protected final void processRequest (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Throwable failureCause = null ; LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext(); LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request); RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor ()); initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes); try { doService(request, response); } catch (ServletException | IOException ex) { failureCause = ex; throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { failureCause = ex; throw new NestedServletException ("Request processing failed" , ex); } finally { resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes); if (requestAttributes != null ) { requestAttributes.requestCompleted(); } logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager); publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause); } }
doService()
所在类:org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 @Override protected void doService (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { logRequest(request); Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null ; if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { attributesSnapshot = new HashMap <>(); Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); if (this .cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) { attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); } } } request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this .localeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this .themeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); if (this .flashMapManager != null ) { FlashMap inputFlashMap = this .flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response); if (inputFlashMap != null ) { request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap)); } request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap ()); request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this .flashMapManager); } RequestPath requestPath = null ; if (this .parseRequestPath && !ServletRequestPathUtils.hasParsedRequestPath(request)) { requestPath = ServletRequestPathUtils.parseAndCache(request); } try { doDispatch(request, response); } finally { if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { if (attributesSnapshot != null ) { restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot); } } if (requestPath != null ) { ServletRequestPathUtils.clearParsedRequestPath(request); } } }
doDispatch()
所在类:org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 protected void doDispatch (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null ; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false ; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null ; Exception dispatchException = null ; try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null ) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return ; } HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET" .equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD" .equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (new ServletWebRequest (request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return ; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return ; } mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return ; } applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } catch (Throwable err) { dispatchException = new NestedServletException ("Handler dispatch failed" , err); } processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException ("Handler processing failed" , err)); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { if (mappedHandler != null ) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } }
processDispatchResult()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 private void processDispatchResult (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv, @Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception { boolean errorView = false ; if (exception != null ) { if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) { logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered" , exception); mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView(); } else { Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null ); mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); errorView = (mv != null ); } } if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { render(mv, request, response); if (errorView) { WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request); } } else { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned." ); } } if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return ; } if (mappedHandler != null ) { mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null ); } }
SpringMVC的执行流程
客户端 (浏览器) 向服务器发送请求,请求被 SpringMVC 前端控制器 DispatcherServlet 捕获。
DispatcherServlet 解析 URL ,得到请求资源标识符 (URI) 并判断 URI 对应的映射。
不存在。
判断是否配置了 mvc:default-servlet-handler,若无,则控制台报映射查找不到,客户端展示 404 错误。若有,则访问目标资源(一般为静态资源,如:JS,CSS,HTML),找不到客户端也会展示 404 错误。
存在。
根据该 URI,调用 HandlerMapping 获得该 Handler 配置的所有相关的对象 (包括 Handler 对象以及 Handler 对象对应的拦截器),最后以 HandlerExecutionChain 执行链对象的形式返回。
DispatcherServlet 根据获得的 Handler ,选择一个合适的 HandlerAdapter 。如果成功获得 HandlerAdapter ,此时将开始执行拦截器的 preHandler(…) 方法 (正向) 。
提取 Request 中的模型数据,填充 Handler 入参,开始执行 Handler (Controller) 方法,处理请求。在填充 Handler 的入参过程中,根据配置,Spring 将执行如下。
HttpMessageConveter: 将请求消息 (如Json、xml等数据) 转换成对象,将对象转换为指定的响应信息。数据转换:对请求消息进行数据转换。如 String 转换成 Integer、Double 等。
数据格式化:对请求消息进行数据格式化。 如将字符串转换成格式化数字或格式化日期等。
数据验证: 验证数据的有效性 (长度、格式等),验证结果存储到 BindingResult 或 Error 中。
Handler 执行完成后,向 DispatcherServlet 返回 ModelAndView 对象。
此时将开始执行拦截器的 postHandle(...) 方法 (逆向)。
根据返回的 ModelAndView (此时会判断是否存在异常:如果存在异常,则执行 HandlerExceptionResolver 进行异常处理) 选择一个适合的 ViewResolver 进行视图解析,根据 Model 和 View ,来渲染视图。
渲染视图完毕执行拦截器的 afterCompletion(…) 方法 (逆向)。
将渲染结果返回给客户端。